Image: Cavalier-Smith - The tree of life and major steps in cell evolution
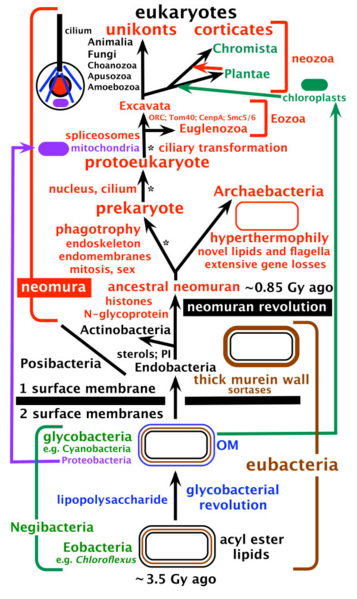
Description: The tree of life and major steps in cell evolution. Archaebacteria are sisters to eukaryotes and, contrary to widespread assumptions, the youngest bacterial phylum. This tree topology, coupled with extensive losses of posibacterial properties by the ancestral archaebacterium, explains (without lateral gene transfer) how eukaryotes possess a unique combination of properties now seen in archaebacteria, posibacteria and a-proteobacteria. Eukaryote origins in three stages indicated by asterisks probably immediately followed divergence of archaebacteria and eukaryote precursors from the ancestral neomuran. This ancestor arose from a stem actinobacterial posibacterium by a quantum evolutionary shake-up of bacterial organization - the neomuran revolution: surface N-linked glycoproteins replaced murein; ribosomes evolved the signal recognition particle’s translational arrest domain; histones replaced DNA gyrase, radically changing DNA replication, repair, and transcription enzymes. The eukaryote depicted is a hypothetical early stage after the origin of nucleus, mitochondrion, cilium, and microtubular skeleton but before distinct anterior and posterior cilia and centriolar and ciliary transformation (anterior cilium young, posterior old) evolved (probably in the cenancestral eukaryote). Kingdom Chromista was recently expanded to include not only the original groups Heterokonta, Cryptista and Haptophyta, but also Alveolata, Rhizaria and Heliozoa, making the name chromalveolates now unnecessary. Excavata now exclude Euglenozoa and comprise just three phyla: the ancestrally aerobic Percolozoa and Loukozoa and the ancestrally anaerobic Metamonada (e.g. Giardia, Trichomonas), which evolved from an aerobic Malawimonas-related loukozoan. Sterols and phosphatidylinositol (PI) probably evolved in the ancestral stem actinobacterium but the ancestral hyperthermophilic archaebacterium lost them when isoprenoid ethers replaced acyl ester lipids.
Title: Cavalier-Smith - The tree of life and major steps in cell evolution
Credit: doi:10.1186/1745-6150-5-7
Author: Thomas Cavalier-Smith
Permission: .mw-parser-output .responsive-license-cc{clear:both;text-align:center;box-sizing:border-box;width:100%;justify-content:space-around;align-items:center;margin:0.5em auto;background-color:#f9f9f9;border:2px solid #e0e0e0;border-spacing:8px;display:flex}.mw-parser-output .responsive-license-cc div{margin:4px}.mw-parser-output .rlicense-text div{margin:0.5em auto}@media screen and (max-width:640px){.mw-parser-output .responsive-license-cc{flex-flow:column}.mw-parser-output .rlicense-text{order:1}} This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 Generic license. You are free: to share – to copy, distribute and transmit the work to remix – to adapt the work Under the following conditions: attribution – You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0CC BY 2.0 Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 truetrue
Usage Terms: Creative Commons Attribution 2.0
License: CC BY 2.0
License Link: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0
Attribution Required?: Yes
Image usage
The following page links to this image:

