Image: Staphylococcus aureus biochemical tests for identification
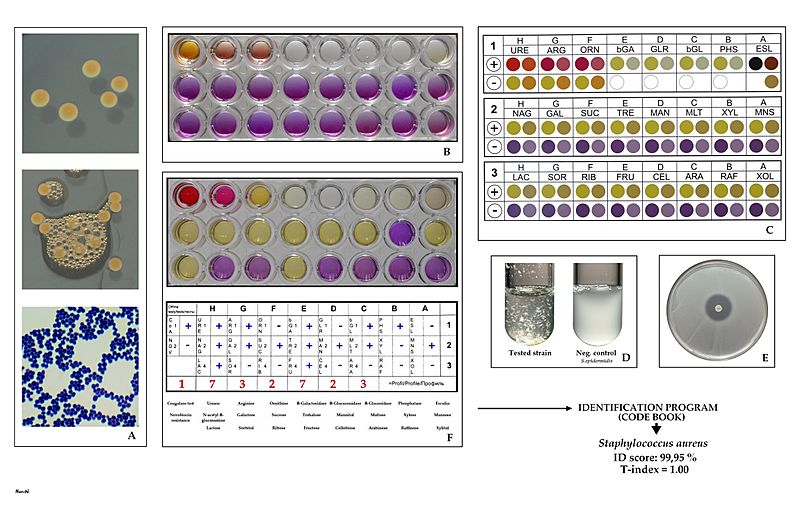
Description: S. aureus can be identified on the basis of several key characteristics. Most strains produce pigmented, smooth, entire, slightly raised colonies about 3 mm in diameter after 24 h of incubation at 37°C. They are catalase positive and stain Gram positive, typically forming cocci in clusters (Fig. A). A widely used criterion for the identification of S. aureus in the clinical laboratory is the clotting of plasma proven by detection of the extracellular free coagulase by the tube test (Fig. D) and detection of the cell wall-bound coagulase (the clumping factor) by the slide agglutination test. The metabolism of staphylococci is respiratory and fermentative. For standardization and convenience, the classical tests for fermentation/oxidation, degradation, and hydrolysis of various substrates have been incorporated into commercial biochemical test systems. A battery of these tests typically occur in the strip format and represent an overnight methods. In the picture the tests are placed in the wells of a triple strip of divided microwell plate (Fig. B). One triple strip is intended for identification of one strain (24 tests). Identification is supplemented with the free coagulase test (Fig. D) and the test of resistance to novobiocin (Fig. E). Procedure is as follows. From pure 24 hour culture is prepared a suspension in sterile saline with a turbidity equal to McFarland No. 2 turbidity scale and 100 µl of the suspension is inoculated in all wells of plate (Fig.B). After incubation at 37°C for 20-24 hours the reactions are in accordance with color chart (Fig. C) and recorded in the result form (Fig. F). A biochemical profile is created by recording the positive and negative test results which can then be compared to an established database. This process is referred to as numerical taxonomy. A higher value indicates greater confidence in the correlation between the unknown and an established identification (or accepted profile). Pre-determined levels of confidence may identify the unknown to the genus or species level depending on the strength of the value obtained (ID score). In this case the probability of the tested species to be Staphylococcus aureus is 99.95%. The T-index represents the biotype validity and it is an expression of the "typicality" of the isolate compared to the species in which it is placed. A biotype validity of 1.00 indicates that the results of the isolate are an exact match to the type species.
Title: Staphylococcus aureus biochemical tests for identification
Credit: Own work
Author: HansN.
Usage Terms: Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0
License: CC BY-SA 4.0
License Link: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0
Attribution Required?: Yes
Image usage
The following page links to this image:

