Inheritance (computer science) facts for kids
In Object-oriented programming languages, inheritance is a powerful way to build computer programs. It's like passing down traits from a parent to a child. Imagine you have a main blueprint for something, like a "Vehicle." Then, you can make new blueprints, like "Car" or "Motorcycle," that automatically get all the basic features from "Vehicle" (like having wheels or being able to move). This saves a lot of work and makes programs easier to manage.
Contents
What is Inheritance in Programming?
In object-oriented programming, we use "classes" as blueprints for creating things called "objects." Think of a class as a cookie cutter. You use it to make many cookies (objects) that are all similar.
When we talk about inheritance, one class, called a derived class (or child class), gets most of its features and actions from another class, called its parent class (or base class).
The child class can then do a few cool things:
- It can add brand new features (called "fields") or actions (called "methods").
- It can change how the existing features or actions from the parent class work.
This means you don't have to write the same code over and over again. You just build on what's already there!
Why Do We Use Inheritance?
Inheritance helps programmers solve different kinds of problems and makes code much neater.
Making Things More Specific
One main reason to use inheritance is for specialization. This is when a child class adds more specific details to what the parent class already has.
- For example, a "Bank account" class might have basic information like "balance," "account number," and "owner."
- Then, a child class called "Interest-earning account" could inherit all those basic details and then add new ones, like "interest rate" and "interest received." It's a more specific type of bank account.
Changing How Things Work
Another use is overriding. This means the child class can redefine or change how an action from the parent class behaves.
- Imagine a "Vehicle" class has a "start engine" action.
- A "Electric Car" child class might override this action so that "start engine" means turning on an electric motor silently, instead of a noisy gasoline engine.
Reusing Code Easily
Inheritance is also great for code reuse. If many different classes need the same features or actions, you can put that common code into a parent class. Then, all the child classes can simply inherit it. This avoids copying and pasting code, which can lead to mistakes and makes updates harder.
An Example: Cars and Their Brands
Let's look at an example using cars.
- You could create a general "Car" class. This class would have common features like "color" and actions like "drive" and "brake."
- Then, you could create a "Ferrari" class and a "Toyota" class. Both of these would inherit from the "Car" class.
- This means all the features and actions from "Car" (like the "drive" method, "brake" method, and "color" field) would automatically be part of the "Ferrari" and "Toyota" classes. You wouldn't need to write that code twice!
However, you might want a "brand" field in your "Car" class. This field might be empty in the general "Car" class. But in the "Ferrari" class, this field would automatically be set to "Ferrari," and in the "Toyota" class, it would be "Toyota."
What is an Abstract Class?
Sometimes, you might not want people to create a general "Car" object directly, because it's too vague (it's missing a specific brand, for example). You only want them to create specific types of cars, like "Ferrari" or "Toyota."
To prevent someone from just creating a "Car" object, you can turn the "Car" class into an abstract class. An abstract class is like a blueprint that's not quite finished. You can't build an actual object directly from an abstract class. You can only use it as a base for other classes to inherit from. This ensures that only complete, specific car types can be created.
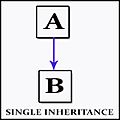
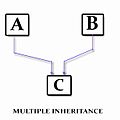
Visual Examples
See also
 In Spanish: Herencia (informática) para niños
In Spanish: Herencia (informática) para niños