Parallel projection facts for kids
A projection is like casting a shadow or drawing a 3D object onto a flat surface. Imagine shining a flashlight on your hand: the shadow on the wall is a projection of your hand. In math, a projection is a special kind of transformation that takes a shape or object and maps it onto a smaller space, like a line or a flat surface.
When you project something, the original object might be in 3D space, but its projection ends up in a 2D space (like a picture) or even a 1D space (like a line). Points that are already on the target surface stay exactly where they are.
Contents
What is a Projection?
A projection is a way to represent something from a higher dimension in a lower dimension. Think of it as squishing or flattening an object. For example, a 3D cube can be projected onto a 2D piece of paper. This is how artists draw realistic 3D scenes.
Projections in Daily Life
You see projections all the time!
- Shadows: When light hits an object, it creates a shadow. The shadow is a projection of the object onto the ground or a wall.
- Movie Projectors: A movie projector takes a small image from a film or digital file and projects a much larger image onto a screen.
- Maps: A map of the Earth is a projection. The Earth is a 3D sphere, but a map is a flat, 2D representation of it.
Drawing 3D Objects: Graphical Projections
In art and engineering, projections are used to draw 3D objects on a 2D surface. This helps people see what a building or a product will look like. There are different ways to do this:
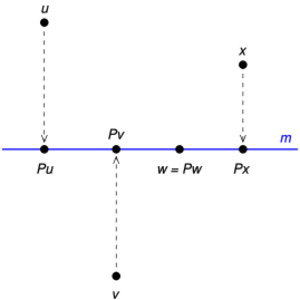
Parallel Projection
In a parallel projection, all the lines that go from the object to the drawing surface are parallel to each other. This means objects that are further away don't look smaller. It's often used for technical drawings because it keeps the true size and shape of parallel lines.
Perspective Projection
Perspective projection is more like how our eyes see the world. Lines from the object meet at a single point, called the "viewpoint." This makes objects that are further away look smaller, just like they do in real life. This method is used a lot in art and photography to create realistic images.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Proyección paralela para niños
In Spanish: Proyección paralela para niños