Raoult's law facts for kids
Raoult's law is a science rule that helps us understand how liquids behave when they mix. It's mostly about something called vapor pressure. Imagine a liquid in a closed bottle. Some of the liquid turns into a gas (vapor) above it. The pressure this gas creates is called vapor pressure.
This law has two main parts. First, if you add something that doesn't easily turn into a gas (like sugar or salt) to a liquid, the liquid's vapor pressure goes down. The more of that "non-volatile" stuff you add, the lower the vapor pressure becomes. It's like the added stuff gets in the way of the liquid turning into gas.
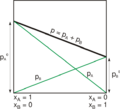
Second, if you mix two liquids that both easily turn into gas, Raoult's law helps predict the total vapor pressure of the mixture. It says that each liquid contributes to the total pressure based on how much of it is in the mix and how easily it turns into gas on its own.
Contents
What is Vapor Pressure?
Think about a pot of water on the stove. When it gets hot, you see steam rising. That steam is water turning into a gas. Even at room temperature, some water molecules escape into the air as gas. In a closed container, these gas molecules create pressure. This is called vapor pressure. Different liquids have different vapor pressures. Liquids that evaporate easily, like rubbing alcohol, have high vapor pressure. Water has a lower vapor pressure.
Understanding Mole Fraction
To understand Raoult's law, you need to know about mole fraction. It's a way to measure how much of one substance is in a mixture compared to everything else. Imagine you have a bag of marbles with red and blue ones. The mole fraction of red marbles would be the number of red marbles divided by the total number of all marbles. In chemistry, we use "moles" instead of counting individual molecules, because molecules are tiny! So, mole fraction tells us the proportion of a substance in a solution.
How Raoult's Law Works
When you add a non-volatile substance (like sugar) to a solvent (like water), the sugar molecules take up space at the surface of the water. This means fewer water molecules are at the surface, ready to escape into the air as vapor. Because fewer water molecules can escape, the vapor pressure of the water goes down.
Raoult's law helps us calculate exactly how much the vapor pressure will drop. It says that the drop in vapor pressure is directly related to the mole fraction of the non-volatile substance you added. The more sugar you add, the lower the water's vapor pressure will be.
If you mix two volatile liquids, like water and alcohol, both liquids will contribute to the total vapor pressure. Raoult's law helps predict the total pressure by adding up the individual pressures of each liquid, adjusted by their mole fractions in the mixture.
Real-World Examples
Raoult's law is important in many areas:
- Chemistry labs: Scientists use it to understand how different chemicals mix and react.
- Distillation: This is a process used to separate liquids, like making pure water from salty water. Raoult's law helps predict how liquids will separate when heated.
- Antifreeze: Adding antifreeze to a car's radiator lowers the freezing point of the water and also changes its boiling point. This is related to how the added substance changes the water's vapor pressure.
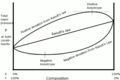
Sometimes, real mixtures don't perfectly follow Raoult's law. This happens when the molecules in the mixture interact strongly with each other, either attracting or repelling each other more than they would on their own. These are called "deviations" from Raoult's law.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Ley de Raoult para niños
In Spanish: Ley de Raoult para niños