Albedo facts for kids
Albedo is a scientific term that describes how much light a surface reflects. Think of it like a mirror, but for all kinds of light, not just what you see. It's a way to measure how shiny or dull something is when light hits it.
Albedo is a number, usually between 0 and 1. A surface with an albedo of 0 reflects no light at all; it absorbs everything. A surface with an albedo of 1 reflects all the light that hits it. Most things have an albedo somewhere in between. The word "albedo" comes from the Latin word albus, which means "white."
What is Albedo?
Albedo measures the amount of light that bounces off a surface compared to how much light hits it. This light can be from the sun or another source. It's a "unitless" measure, meaning it's just a number, not something like meters or kilograms.
For example, a bright white surface, like fresh snow, has a high albedo. This means it reflects a lot of sunlight. A dark surface, like asphalt or a forest, has a low albedo. It absorbs most of the sunlight that hits it.
Why Albedo Matters
Albedo is very important for understanding our planet's climate. When sunlight hits Earth, some of it is reflected back into space. The rest is absorbed by the land, oceans, and atmosphere. This absorbed energy warms the planet.
- Climate Change: Changes in Earth's albedo can affect global temperatures. If more ice melts, Earth's albedo goes down. This means more sunlight is absorbed, leading to more warming.
- Urban Areas: Cities often have dark roofs and roads. These surfaces absorb a lot of heat, making cities hotter than surrounding rural areas. This is known as the "urban heat island" effect.
- Planetary Science: Scientists also study the albedo of other planets and moons. This helps them learn about their surfaces and atmospheres. For instance, Venus has a very high albedo because of its thick, reflective clouds.
Examples of Albedo
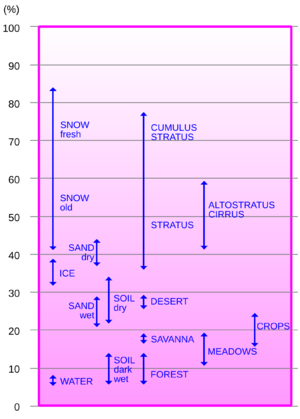
Different surfaces have different albedo values:
- Fresh Snow: Has a very high albedo, usually between 0.8 and 0.9. This means it reflects 80% to 90% of sunlight.
- Old Snow or Ice: Has a slightly lower albedo, around 0.5 to 0.7.
- Clouds: Can have a high albedo, reflecting a lot of sunlight back into space.
- Forests: Have a low albedo, typically between 0.1 and 0.2. They absorb most sunlight.
- Oceans: Also have a low albedo, especially when the sun is high in the sky. They absorb a lot of heat.
- Asphalt Roads: Are very dark and have a low albedo, often around 0.05 to 0.1.
Understanding albedo helps us see how different parts of our world interact with sunlight. It also shows how human activities, like building cities or cutting down forests, can impact the planet's temperature.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Albedo para niños
In Spanish: Albedo para niños