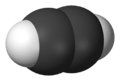Alkyne facts for kids
An alkyne is a special type of molecule that has a very strong connection, called a 'triple bond,' between two carbon atoms. They follow a general chemical formula: CnH2n-2. This formula helps scientists know how many carbon and hydrogen atoms are in them. You might also hear them called 'acetylenes.' The smallest alkyne is called acetylene, or sometimes 'ethyne.' Alkynes are 'hydrophobic.' This means they don't mix well with water, but they can easily dissolve in other liquids like oils or gasoline (called 'organic solvents').
Alkynes are quite reactive, meaning they like to participate in chemical reactions. They are even more reactive than other similar molecules called 'alkenes.' If an alkyne is at the end of a molecule, it's easy to remove a tiny part called a 'proton' using a strong chemical 'base.' This makes the alkyne ready for 'addition reactions,' where other atoms or molecules can join it. For example, they can be added to a type of molecule called a 'ketone.' Alkynes can also be 'reduced,' which means they can be changed into molecules with 'double bonds.' These double bonds can be arranged in two different ways: 'trans' or 'cis.' Scientists also use alkynes a lot in special reactions called 'pericyclic reactions.'
The Shape of Alkynes
The two carbon atoms in an alkyne's triple bond are arranged in a straight line, forming a 180-degree angle. Because of this straight shape, alkynes don't usually form ring-shaped molecules (called 'cyclic compounds').
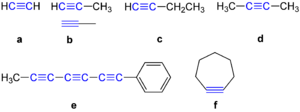
Examples of Alkynes
Here are some examples of what alkynes look like:
Images for kids
-
A 3D model of ethyne (acetylene), the simplest alkyne
See also
 In Spanish: Alquino para niños
In Spanish: Alquino para niños