Autophagy facts for kids
Autophagy (say "aw-TOFF-uh-jee") is a super important process inside your body's cells. It means "eating itself," which sounds a bit strange! But it's actually how cells clean up and recycle their old or broken parts. Think of it like a tiny recycling plant inside each of your cells. This process helps keep your cells healthy and working well.
What is Autophagy?
Autophagy is a basic way cells stay healthy. It helps them get rid of parts that don't work anymore or aren't needed. After breaking down these old parts, the cell can reuse the materials to build new ones. This is very efficient, just like recycling plastic bottles to make new ones!
How Does Autophagy Work?
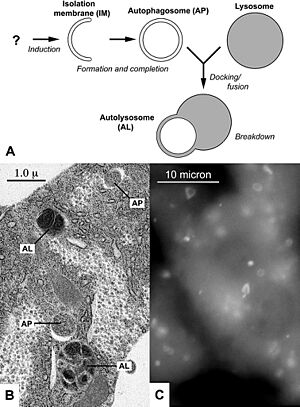
When a cell needs to clean up, it finds the parts that need to go. These parts are then wrapped up in a special bubble called an autophagosome. This bubble has a double wall, like a tiny balloon inside another balloon.
Next, the autophagosome bubble joins up with another part of the cell called a lysosome. Lysosomes are like the cell's "stomachs" because they contain strong chemicals that can break things down. Once the autophagosome and lysosome join, the old cell parts inside are broken down into tiny pieces. These tiny pieces can then be used again by the cell to make new parts or to get energy.
Sometimes, if a cell doesn't have enough food, autophagy becomes even more important. It helps the cell survive by breaking down some of its own parts to create energy. This is like when your body uses stored fat for energy if you haven't eaten in a while.
The Discovery of Autophagy
The word "autophagy" was first used by a Belgian scientist named Christian de Duve in 1963. For many years, scientists knew it happened but didn't fully understand how.
In the 1990s, researchers started studying autophagy in yeast. Yeast are tiny, single-celled organisms, and they are great for studying how cells work. By studying yeast, scientists were able to find the specific genes that control autophagy. This helped them figure out exactly how the process works step-by-step.
This important research led to a big award! In 2016, a Japanese scientist named Yoshinori Ohsumi won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his discoveries about how autophagy works. His work helped us understand how cells recycle themselves and how this process is important for our health.
See also
 In Spanish: Autofagia para niños
In Spanish: Autofagia para niños
 | Precious Adams |
 | Lauren Anderson |
 | Janet Collins |