Bank of United States facts for kids
The Bank of United States was a bank in New York City. It was started by Joseph S. Marcus in 1913. Sadly, the bank failed in 1931. Many people believe its failure helped start the big banking crisis during the Great Depression. This happened when many people rushed to withdraw their money from the bank.
Contents
How the Bank of United States Started
The Bank of United States officially began on June 23, 1913. It was founded by Joseph S. Marcus. He was a successful banker who had disagreements with his old bank. He wanted to start a new one.
The name "Bank of United States" caused some arguments. Other bankers worried that people, especially new immigrants, might think it was a government bank. They feared people would believe it was part of the U.S. Treasury. But the name was approved anyway. Later, in 1926, it became illegal to use such a name for a private bank. However, this rule did not apply to banks already using the name.
Joseph S. Marcus, the founder, was an immigrant from Germany. He came to the United States when he was 17. He started as a tailor and worked his way up. He became a successful businessman in the clothing industry. Then he became a banker. He also gave a lot of money to hospitals and charities. He passed away in 1927.
His son, Bernard K. Marcus, joined the bank in 1913. He became a vice president in 1918.
Growing Big: The Bank's Expansion
At first, the Bank of United States grew slowly. By 1925, it only had five branches. After Joseph S. Marcus died, his son Bernard took over. Bernard helped the bank grow very quickly. He did this by merging with other banks. By 1930, the bank had 62 branches!
In 1928, it merged with the Central Mercantile Bank and Trust Company. Bernard Marcus became the president. Later that year, it also joined with the Cosmopolitan Bank.
More mergers happened in 1929. The Bank of United States absorbed the Colonial Bank and the Bank of the Rockaways. In May 1929, it merged with the Municipal Bank and Trust Company. This made the Bank of United States the third largest bank in New York City. It was the twenty-eighth largest in the entire United States.
After the Wall Street Crash of 1929 (also known as Black Tuesday), the bank's president told shareholders the bank was strong. But things were about to change.
In 1930, the Bank of United States and three other big New York banks talked about merging. They wanted to form a huge "mega-bank." But the plan fell apart in December 1930. There were problems with guaranteeing deposits and issues with the bank's loans. Just two days later, people started rushing to one of the bank's branches.
Why the Bank Failed
On December 10, 1930, a huge crowd gathered at a Bank of United States branch in the Bronx. They all wanted to take their money out. This event is often seen as the start of the "bank runs" during the Great Depression. A bank run happens when many people try to withdraw their money at the same time.
News reports said the run started because of a false rumor. A local merchant claimed the bank would not sell his stock. Soon, 20,000 to 25,000 people gathered. Police had to control the crowd. By the end of the day, about $2 million was withdrawn. But most people who came to the bank still left their money there.
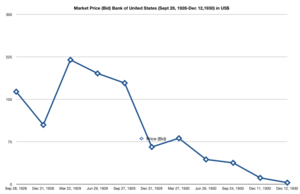
The next day, the bank's leaders feared more people would try to withdraw money. So, they decided to close the bank. They asked the Superintendent of Banks to take control. The bank's stock price dropped very quickly. It went from $11.50 to just $3.00. Other bank stocks also fell.
Officials tried to arrange a merger with other banks to save it. But the big banks on Wall Street refused to help. Without a large loan, the Bank of United States could not be saved.
The closing of the Bank of United States was a big shock. It was the first time such a large New York bank had failed since 1907. City and state officials tried to calm the public. They quickly set up a program. This program allowed Bank of United States depositors to borrow money against their deposits. People lined up for hours to get these loans.
What Happened Next
The failure of the Bank of United States had a huge impact. It was one of 608 banks that closed in late 1930. The Bank of United States alone accounted for one-third of all the money lost in these bank failures. Its closure made people even more scared. They rushed to withdraw their money from other banks too.
To stay open, banks had to ask for loans back and sell their assets. In just one month, over 300 banks across the country failed. This made the Great Depression even worse.
After the bank closed, its main building on Delancey Street was taken over. It became the home of the Hebrew Publishing Company in 1932.
 | Calvin Brent |
 | Walter T. Bailey |
 | Martha Cassell Thompson |
 | Alberta Jeannette Cassell |