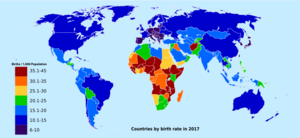
Birth rate facts for kids
The birth rate, also called natality, tells us how many babies are born in a certain place over a specific time. It's usually measured as the number of live births for every 1,000 people in a population.
To figure out the birth rate, experts count all the live births in a year. They also count how many people live in that area. This helps them understand how fast a population is growing or shrinking.
The birth rate is super important for understanding population growth. When you combine it with the mortality rate (how many people die) and human migration (people moving in or out), you can see how a population changes over time.
When the number of deaths (the crude death rate) is taken away from the number of births (the crude birth rate, or CBR), you get the rate of natural increase (RNI). This RNI shows how much a population changes just from births and deaths, not counting people moving.
| Years | CBR | Years | CBR |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1950–1955 | 36.9 | 2000–2005 | 21.0 |
| 1955–1960 | 35.4 | 2005–2010 | 20.3 |
| 1960–1965 | 35.2 | 2010–2015 | 19.5 |
| 1965–1970 | 34.0 | 2015–2020 | 18.5 |
| 1970–1975 | 31.4 | 2020–2025 | 17.5 |
| 1975–1980 | 28.5 | 2025–2030 | 16.6 |
| 1980–1985 | 27.7 | 2030–2035 | 16.0 |
| 1985–1990 | 27.4 | 2035–2040 | 15.5 |
| 1990–1995 | 24.2 | 2040–2045 | 15.0 |
| 1995–2000 | 22.2 | 2045–2050 | 14.6 |
In 2021, the average birth rate around the world was about 18.1 births for every 1,000 people. The death rate was 7.7 per 1,000. This means the world's population grew by about 1.6 percent that year, not counting people moving between countries.
To give you an idea, 18.1 births per 1,000 people means roughly 4.3 babies are born every second worldwide! That's about 259 births every minute.
What affects birth rates?
Many things can influence how many babies are born in a country or region. These factors often work together in complicated ways.
- Developed vs. Developing Countries: Countries that are more developed (like the USA or Japan) usually have lower birth rates. Countries that are still developing often have higher birth rates.
- Education and Wealth: Generally, as people get more education and become wealthier, families tend to have fewer children.
- Women's Roles: When women have more rights and opportunities to work outside the home, birth rates often go down.
- City vs. Country: People living in cities often have fewer children than those living in rural areas.
- Age: The age of parents, especially mothers, can affect birth rates. Older mothers tend to have fewer children.
It's important to remember that these are general trends. The exact reasons for birth rate changes can be different in various parts of the world and among different groups of people.
See also
- Population ageing
- Population decline
 In Spanish: Tasa bruta de natalidad para niños
In Spanish: Tasa bruta de natalidad para niños
 | Selma Burke |
 | Pauline Powell Burns |
 | Frederick J. Brown |
 | Robert Blackburn |