Boronia wilsonii facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Boronia wilsonii |
|
|---|---|
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Sapindales |
| Family: | Rutaceae |
| Genus: | Boronia |
| Species: |
B. wilsonii
|
| Binomial name | |
| Boronia wilsonii |
|
 |
|
| Occurrence data from Australasian Virtual Herbarium | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The Boronia wilsonii is a type of shrub that stands upright. It is found only in northern Australia. Its branches, leaves, and the back of its flowers are covered in soft, woolly hairs. The petals of its flowers can be white, pink, or a deep red (burgundy) color.
Contents
What Does Boronia wilsonii Look Like?
Boronia wilsonii is an upright shrub. It usually grows to be about 0.3 to 1.5 meters (about 1 to 5 feet) tall. Young plants have a moderate amount of woolly, star-shaped hairs. These hairs are found on their branches and leaves. As the plant gets older, these hairs become very dense. They cover the branches, leaves, and even the back of the flowers.
Leaves and Flowers
The leaves of this plant are "pinnate." This means they have many smaller leaflets arranged along a central stem, like a feather. Each leaf is about 17 to 34 millimeters long. They have between thirteen and twenty-three small leaflets. Each leaflet is shaped like an ellipse or a spear tip. They are about 1.5 to 23 millimeters long and 1 to 6 millimeters wide. The leaves grow on a short stalk called a petiole, which is about 0.5 to 7 millimeters long.
The flowers usually grow one by one. Each flower sits on a small stalk called a pedicel, about 2.5 to 7 millimeters long. The sepals are the green, leaf-like parts that protect the flower bud. They are larger than the petals. Sepals are egg-shaped or triangular, about 5 to 10 millimeters long and 2 to 4.5 millimeters wide. Their backs are very hairy. The petals themselves are white, pink, or burgundy. They are about 4 to 6 millimeters long. Both the sepals and petals grow larger as the fruit starts to form.
When Does it Flower and What About its Fruit?
Boronia wilsonii flowers between January and September. After flowering, it produces a fruit. This fruit is a hairy "capsule." A capsule is a dry fruit that splits open to release seeds. The capsule is about 4.5 to 6 millimeters long and 2 to 2.5 millimeters wide.
How Did Boronia wilsonii Get its Name?
This boronia plant was first officially described in 1863. A scientist named George Bentham wrote about it. He used notes from another scientist, Ferdinand von Mueller. Mueller had first called it Boronia artemisiifolia var. wilsonii. This description was published in a book called Flora Australiensis.
Later, in 1997, a botanist named Marco Duretto changed its classification. He decided it was a unique species on its own. So, he gave it the name Boronia wilsonii. The second part of its name, wilsonii, honors an early collector of the plant. This person was likely James Spottiswoode Wilson. He was a geologist who explored northern Australia with Mueller in 1855-1856.
Where Does Boronia wilsonii Grow?
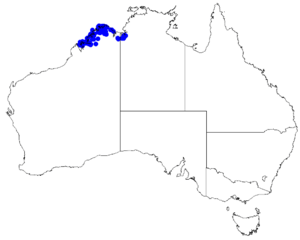
Boronia wilsonii is commonly found in the Kimberley region of Western Australia. It also grows on islands nearby. It prefers to grow in sandy soil, usually over sandstone, close to the coast. You can also find a few collections of this plant near the lower Victoria River in the Northern Territory.
Is Boronia wilsonii Protected?
The conservation status of a plant tells us how much it is at risk. In Western Australia, the government's Department of Parks and Wildlife says this species is "not threatened." This means it is not currently at risk of disappearing. However, in the Northern Territory, it is listed as "near threatened." This means it could become threatened in the future if conditions change. This classification is under the Territory Parks and Wildlife Conservation Act 2000.
 | Precious Adams |
 | Lauren Anderson |
 | Janet Collins |

