Brain-eating amoeba facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Naegleria fowleri |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
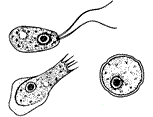
| Different stages of Naegleria fowleri | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | |
| (unranked): | |
| Phylum: |
Percolozoa
|
| Class: |
Heterolobosea
|
| Order: |
Schizopyrenida
|
| Family: |
Vahlkampfiidae
|
| Genus: |
Naegleria
|
| Species: |
N. fowleri
|
| Binomial name | |
| Naegleria fowleri Carter (1970)
|
|
Naegleria fowleri is a tiny living creature, a type of protist, often called the "brain-eating amoeba." It lives in warm fresh water, usually between 25 and 35 degrees Celsius (77–95 degrees Fahrenheit). This amoeba belongs to a group called Percolozoa.
While very rare, N. fowleri can cause a serious infection if it enters a person's nose. This infection affects the brain and is almost always fatal.
Contents
What is Naegleria fowleri?
Naegleria fowleri is a single-celled organism. It is so small you need a microscope to see it. It is a type of amoeba, which means it moves and feeds by changing its shape.
This amoeba has three main forms during its life. It can be a cyst (a tough, resting stage), a trophozoite (the feeding and growing stage), or a flagellate (a swimming stage with whip-like tails). The trophozoite stage is the one that can cause infection.
Where Does This Amoeba Live?
Naegleria fowleri loves warm freshwater environments. You can find it in places like:
- Lakes and ponds
- Rivers
- Hot springs
- Untreated swimming pools
- Water heaters
- Soil
It does not live in salt water, like the ocean. It also cannot survive in properly treated swimming pools or tap water that has enough chlorine.
How Does It Cause Sickness?
Infection with Naegleria fowleri is very rare. It happens when water containing the amoeba goes up a person's nose. This usually occurs when someone swims, dives, or jumps into warm freshwater.
Once in the nose, the amoeba travels to the brain. It then causes a severe brain infection called Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM). It is important to know that you cannot get infected by drinking water that contains Naegleria fowleri. The amoeba must enter through the nose.
What Are the Symptoms of PAM?
Symptoms of Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM) usually start about 1 to 9 days after exposure. They can include:
- Severe headache
- Fever
- Stiff neck
- Vomiting
As the infection gets worse, people might experience:
- Confusion
- Lack of attention to their surroundings
- Seizures
- Hallucinations
- Coma
Sadly, PAM progresses very quickly. It almost always leads to death within about 5 to 18 days after symptoms begin.
How Rare is This Infection?
Infections from Naegleria fowleri are extremely rare. For example, in the United States, there have been only a few dozen cases over many decades. You are much more likely to be struck by lightning than to get infected with this amoeba.
How Can You Stay Safe?
Even though it's rare, there are ways to reduce your risk of infection:
- Avoid swimming in warm freshwater during very hot weather, especially in stagnant or poorly circulated water.
- Hold your nose or use nose clips when jumping, diving, or doing water sports in warm freshwater.
- Avoid stirring up sediment in shallow areas of warm freshwater. The amoeba often lives in the mud and sand at the bottom.
- Use only sterile water for nasal rinses, like with a neti pot. You can buy sterile water or boil tap water for at least 1 minute and let it cool.
Remember, treated tap water and properly chlorinated swimming pools are generally safe.
Images for kids
-
Roman Baths in Bath, Somerset, closed for bathing since 1978 due to presence of N. fowleri
See also
 In Spanish: Naegleria fowleri para niños
In Spanish: Naegleria fowleri para niños


