CT scan facts for kids
A CT scan (short for computed tomography scan) is a special type of medical imaging that helps doctors see detailed pictures of the inside of your body. Think of it like taking many X-ray pictures from different angles, and then a computer puts them all together to create "slices" or cross-sections of your body. These slices show organs, bones, and tissues in great detail.
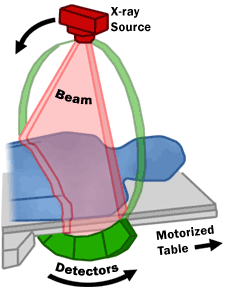
CT scanners use a spinning X-ray tube and special detectors. As the X-rays pass through your body, different tissues block the X-rays by different amounts. A computer then uses this information to build the detailed images. CT scans are very useful because they can show things that regular X-rays might miss. They can also be used for people who have metal implants or pacemakers, unlike magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Since it was invented in the 1970s, CT scanning has become a super important tool in medicine. It's mostly used to help doctors figure out what's going on inside a patient's body. But it can also be used to look at non-living things! The people who invented this amazing technology, Allan MacLeod Cormack and Godfrey Hounsfield, even won a Nobel Prize in 1979 for their work.
How Do CT Scanners Work?
There are different kinds of CT scanners, each with its own way of taking pictures.
Sequential CT
Imagine taking a picture, moving a little, stopping, taking another picture, and so on. That's how sequential CT works. The patient's bed moves step-by-step, and the X-ray machine takes one "slice" at a time. This method can take a bit longer.
Spiral CT
Most CT scanners today are "spiral" or "helical" CTs. Instead of stopping and starting, the X-ray tube spins continuously around the patient while the bed moves smoothly through the scanner. This creates a spiral path for the X-rays. Spiral CTs are very common because they are efficient and can scan faster.
Electron Beam Tomography
This is a special type of CT where only the electron beam inside the X-ray tube moves very quickly. This makes it super fast, which is great for imaging things that move a lot, like your heart and arteries. It helps get clearer pictures without blur.
Dual Energy CT
Dual Energy CT uses two different X-ray energies at the same time. This allows the scanner to collect more information about the tissues. It can use two X-ray tubes or switch energies very quickly with one tube. This helps doctors see different materials in the body more clearly and can reduce motion blur, especially for the heart.
CT Perfusion Imaging
This type of CT helps doctors see how blood flows through your blood vessels. A special liquid called a contrast agent is injected, and the CT scan tracks its movement. This can show how much blood is reaching organs like the brain or heart. It's especially helpful for diagnosing problems like a stroke.
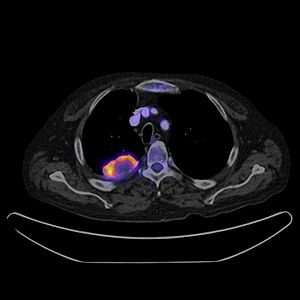
PET CT
PET-CT combines two powerful imaging methods: PET (positron emission tomography) and CT. A PET scan shows how active your body's cells are, which can reveal problems like cancer. A CT scan shows detailed anatomy. By combining them, doctors get both a functional view (what the cells are doing) and an anatomical view (where they are in the body) in one image. This helps in finding and understanding different types of cancers.
Medical Uses of CT Scans
CT scans are a very important tool in medicine, helping doctors diagnose and treat many conditions.
Head
CT scans of the head are often used to check for things like stroke, tumors, bleeding, or bone injuries. Doctors can see if there's swelling or if bones are broken. It's also used to guide surgeries for brain tumors.
Neck
If someone has a lump in their neck, a CT scan is usually one of the first tests doctors use to find out what it is. It's also important for checking the thyroid gland.
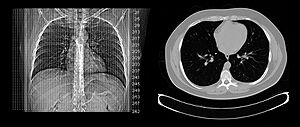
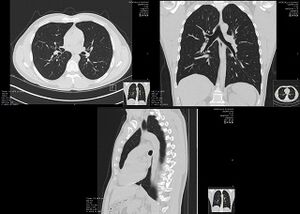
Lungs
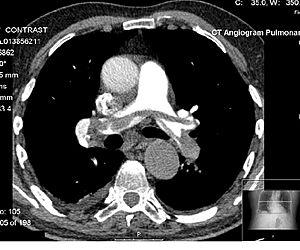
CT scans are great for looking at the lungs because they can show tiny changes that regular X-rays might miss. They can help find conditions like emphysema or fibrosis. Sometimes, a CT scan might find a small spot in the lung that wasn't expected. Doctors have guidelines for how often to check these spots, as too many CT scans can expose a person to more radiation than needed.
Angiography
Computed tomography angiography (CTA) is a CT scan that focuses on your blood vessels. A special dye is injected into your veins, which makes the arteries and veins show up brightly on the scan. This helps doctors find blockages or other problems in blood vessels all over the body, like in the lungs or legs.
Heart
CT scans of the heart help doctors understand the heart's structure and its blood vessels.
- Coronary CT angiography (CCTA): This scan uses dye to look at the arteries that supply blood to your heart. It helps doctors see if there are any blockages that could lead to heart disease.
- Coronary CT calcium scan: This scan looks for calcium deposits in your heart's arteries. Calcium can build up and narrow the arteries, increasing the risk of a heart attack. This scan usually doesn't need a dye.
Doctors often use computers to create 3D models of the heart from these scans, which helps them plan treatments.
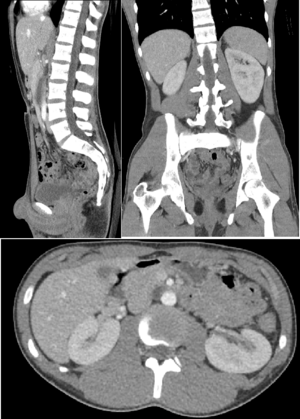
Abdomen and Pelvis
CT scans are very good at diagnosing problems in the belly area, like Crohn's disease or bleeding. They are also used to find and check on cancers. If someone has bad belly pain, a CT scan is often used to find the cause. It's also the best way to find kidney stones and see their size and location.
Bones and Joints
For complex bone breaks, especially around joints, CT scans are very helpful. They can show the injury from many angles, making it easier for doctors to see exactly what happened. They can also help diagnose conditions like gout.
Other Uses of CT Scans
CT scans aren't just for people! They have many other cool uses.
Industrial Use
In factories, CT scans are used to look inside objects without breaking them. This helps engineers find flaws, check how parts are put together, or even create 3D models of objects. It's used in many industries.
Aviation Security
You might see CT scanners at airports! They are used to check luggage for dangerous items like explosives or weapons. They can create 3D images of bags, helping security see what's inside more clearly. This technology is helping airports make travel safer and faster.
Geological Use
Scientists use CT scans to look inside rock samples or drill cores. They can see different minerals and materials hidden inside without having to break the rock apart.
Cultural Heritage Use
CT scans are amazing for studying old and fragile artifacts like ancient scrolls or mummies. They let researchers see inside these objects without damaging them. For example, CT scans helped read hidden text inside a burned scroll and understand ancient machines.
Advantages of CT Scans
CT scans offer many benefits compared to regular X-rays:
- Clearer Pictures: CT scans remove the "overlap" of body parts, giving a much clearer view of the area of interest.
- More Detail: They show finer details and can tell the difference between tissues that are only slightly different in density.
- 3D Views: CT scans can create images from different angles (like side views or front views) or even full 3D models, which helps doctors understand complex problems.
Newer CT scans can do things like perform a "virtual colonoscopy," which is more accurate and comfortable than a traditional one.
Important Things to Know About CT Scans
While CT scans are very useful, it's good to know about a few things.
Radiation Exposure
CT scans use X-rays, which are a type of radiation. This radiation can slightly increase the risk of cancer over a person's lifetime. The amount of radiation from a CT scan varies, but it's generally more than a regular X-ray. For example, a CT scan of the belly might give you about the same radiation as you'd naturally get from the environment over three years.
Doctors always try to use the lowest possible radiation dose that still gives a good image, especially for children. The benefits of finding out what's wrong with a CT scan usually outweigh the small risk of radiation, especially when it's medically necessary. However, it's important not to have too many unnecessary CT scans.
Contrast Agent Reactions
Sometimes, a special liquid called a contrast agent is injected into your vein during a CT scan. This helps certain parts of your body, like blood vessels, show up more clearly. Most reactions to this liquid are mild, like feeling sick or having a rash. Serious reactions are very rare.
The contrast agent can sometimes affect the kidneys, especially in people who already have kidney problems. Doctors will check your kidney function before giving you contrast.
How a CT Scan is Done
The process for a CT scan depends on what part of your body is being scanned.
- You'll lie on a special bed that slides into the CT scanner.
- If you need contrast, a nurse will put a small tube into your vein for the liquid.
- The X-ray machine will spin around you, taking pictures. You'll need to stay very still.
- The computer then processes all the pictures to create the detailed images.
Preparation for a CT Scan
Before your CT scan, you might need to do a few things:
- You might be asked to sign a form saying you understand the procedure.
- You'll need to remove any metal objects or jewelry from the area being scanned.
- Sometimes, you'll change into a hospital gown.
- If you're getting contrast, doctors will check your kidney function beforehand.
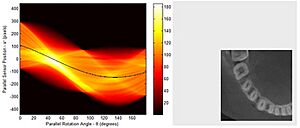
How the Images are Made
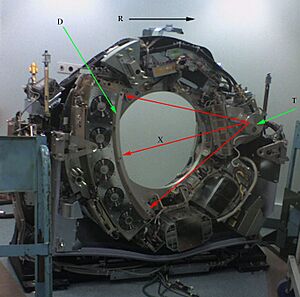
A CT scanner has an X-ray generator that spins around you, and detectors on the other side. As X-rays pass through your body, different tissues block them differently. Bones block more X-rays than soft tissues, for example. The detectors measure how much X-ray energy gets through.
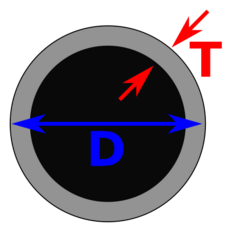
This raw data is then sent to a computer. The computer uses special math to reconstruct all the information into cross-sectional images, like slices of bread. Each tiny square in the image is called a "pixel," and when you add the slice thickness, it becomes a 3D "voxel."
These pixels are shown in different shades of gray based on how much X-ray they blocked. For example, air looks black, water is gray, and bones look white. Doctors look at these shades to understand what's inside your body.
History of CT Scans
The idea behind CT scans goes back to 1917 with mathematical theories. But the first CT scanner that could be used commercially was invented by Godfrey Hounsfield in 1972. It's often said that money from The Beatles' music sales helped fund the early development of CT scanners at a company called EMI, which was also a music company!
The word "tomography" comes from Greek words meaning "slice" and "to write." CT scans were first called "EMI scans" or "CAT scans." Now, doctors usually just say "CT scan" because the machines can create images from many different angles, not just "axial" (cross-sectional) ones.
CT Scans in Society
Safety Campaigns
Because CT scans use radiation, doctors and organizations have created campaigns to make sure they are used safely, especially for children.
- The Image Gently Campaign helps doctors use the lowest possible radiation doses for kids while still getting good images.
- The Image Wisely Campaign does the same for adults.
These campaigns help ensure that CT scans are used wisely and safely.
How Common Are CT Scans?
The use of CT scans has grown a lot over the past 20 years. In the United States, tens of millions of CT scans are done each year. This increase is partly because scanners have become faster and easier to use, even for children. However, some CT scans might be done when they aren't absolutely necessary. Doctors and patients work together to decide when a CT scan is the best choice.
CT Scanner Manufacturers
Some of the big companies that make CT scanning machines are:
- GE Healthcare (USA)
- Siemens Healthineers (Germany)
- Canon Medical Systems Corporation (Japan)
- Koninklijke Philips N.V. (Netherlands)
- Fujifilm Healthcare (Japan)
- Neusoft Medical Systems (China)
- United Imaging (China)
Future of CT Scans
Scientists are always working on making CT scans even better. One exciting area is "photon-counting CT." These new scanners could give even clearer images with less radiation, and help doctors see more details about different tissues. This could lead to even safer and more powerful CT scans in the future!
Images for kids