Cardiomyopathy facts for kids
The word cardiomyopathy means "heart muscle disease." It's a group of conditions where your heart muscle (called the myocardium) doesn't work as well as it should. People with cardiomyopathy can sometimes have heartbeat problems or other serious heart issues.
Contents
What is Cardiomyopathy?
Cardiomyopathy is a medical term for diseases that affect the heart muscle. When your heart muscle is sick, it can't pump blood around your body as well as it normally does. This can lead to different kinds of health problems.
Different Types of Cardiomyopathy
There are four main types of cardiomyopathy. Each one affects the heart in a slightly different way.
Dilated Cardiomyopathy (DCM)
This is the most common type of cardiomyopathy. In DCM, your heart, especially the main pumping chamber called the left ventricle, becomes enlarged and stretched out. This makes it harder for the heart to pump blood effectively. Sometimes, people with severe DCM might need a heart transplant.
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM)
HCM is often a genetic condition, meaning it can run in families. With HCM, the heart muscle gets too thick. This thickening can block blood flow out of the heart or make it harder for the heart to fill with blood.
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy (ARVC)
ARVC is a condition where the heart's electrical system has problems. Over time, some of the heart muscle, usually in the right ventricle, gets replaced by scar tissue. This can cause irregular heartbeats.
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy (RCM)
RCM is the least common type of cardiomyopathy. In this condition, the walls of the heart's pumping chambers (the ventricles) become stiff. Even if they aren't thicker than usual, this stiffness makes it hard for the heart to relax and fill with blood properly.
Images for kids
-
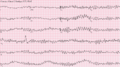
This picture shows ventricular fibrillation, a type of irregular heartbeat, on a heart test called an ECG.
See also
 In Spanish: Miocardiopatía para niños
In Spanish: Miocardiopatía para niños