Carrier-sense multiple access with collision avoidance facts for kids
Carrier-sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA) is a smart way for computers to share a network, especially for wireless networks like Wi-Fi. Imagine many people trying to talk at once on a radio channel. CSMA/CA helps them avoid talking over each other.
It's a method where devices first "listen" to the network to see if anyone else is sending data. If the network is clear, they send their own information. This is different from other methods that try to detect collisions *after* they happen. CSMA/CA tries to *prevent* collisions from happening in the first place.
This method is really important for wireless networks because it's hard for a wireless device to listen and send data at the exact same time. CSMA/CA works at the data link layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model, which is like the traffic cop for data on a network.
Contents
How CSMA/CA Works
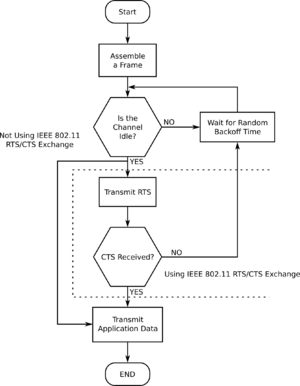
CSMA/CA helps many devices share the same communication path fairly. It tries to make sure everyone gets a turn to send data without their messages crashing into each other.
Listening First (Carrier Sense)
Before a device sends any data, it first "listens" to the shared network channel. This is like checking if the phone line is busy before you dial. If another device is already sending data, the first device waits.
The Hidden Node Problem
Sometimes, a device might not "hear" another device that is sending data. This is called the hidden node problem. For example, in a wireless network, two devices might be able to talk to the main Wi-Fi router, but they can't "hear" each other because they are too far apart or blocked by something. This can still lead to collisions.
Avoiding Collisions (Collision Avoidance)
If the network channel is busy, the device waits for a short, random amount of time. Then it listens again. This random waiting helps prevent many devices from trying to send data at the exact same moment once the channel becomes free.
Request to Send/Clear to Send (RTS/CTS)
To help with the hidden node problem, devices can optionally use a special handshake called Request to Send (RTS) and Clear to Send (CTS).
- A device that wants to send data first sends a small RTS message to the receiver (like a Wi-Fi router).
- If the receiver is ready, it sends back a CTS message.
- This CTS message tells all other devices nearby to "be quiet" for a certain amount of time so the sender can transmit its data without interruption.
- This helps prevent collisions, especially when devices can't hear each other directly.
Sending Data
Once the network channel is clear, or the device receives a CTS message, it sends its entire data packet. After sending, the device waits for a confirmation message (an "acknowledgement") from the receiver. If the acknowledgement doesn't arrive in time, the device assumes the data collided with another transmission. It then waits for a random period before trying to send the data again.
Why CSMA/CA is Good for Wireless Networks
CSMA/CA is very useful for wireless networks (like your home Wi-Fi). This is because wireless devices often have the "hidden node problem." A device might be able to connect to the Wi-Fi router, but it can't "hear" another device connected to the same router. CSMA/CA, especially with RTS/CTS, helps solve this by making sure the router manages who gets to talk and when.
Where CSMA/CA is Used
CSMA/CA is used in many different network technologies:
- Apple's LocalTalk: An older network system used by Apple computers.
- 802.11 RTS/CTS: This is part of how Wi-Fi (IEEE 802.11) networks work. While Wi-Fi mostly "listens" directly, it can use RTS/CTS for virtual listening.
- IEEE 802.15.4: This standard is used for low-power wireless personal area networks (like some smart home devices).
- HomePNA: A technology that uses existing home wiring (like phone lines or coaxial cables) for networking.
- ITU-T G.hn: A standard for high-speed home networks that use power lines, phone lines, and coaxial cables. It uses CSMA/CA for data that doesn't need guaranteed delivery.
See also
 In Spanish: Carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance para niños
In Spanish: Carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance para niños
- Carrier-sense multiple access
- Carrier-sense multiple access with collision detection
- IEEE 802.11 RTS/CTS
- Network allocation vector
- Truncated binary exponential backoff