Computer bus facts for kids
Imagine your computer is a busy city. A computer bus is like the main roads or highways that connect all the important buildings and places. Its job is to move information, electrical signals, and even power between different parts inside your computer. Without buses, the different parts of your computer wouldn't be able to talk to each other!
Contents
What is a Computer Bus?
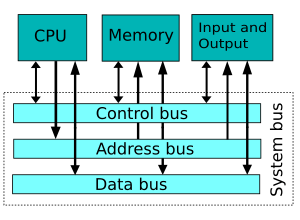
A computer bus is a system that allows data to travel between different parts of a computer. Think of it as a set of wires or connections. These connections carry information, like instructions or numbers, from one place to another. They also carry signals that tell parts when to start or stop. Sometimes, they even carry electrical power.
How Wide is a Bus?
The size or width of a bus tells you how much information it can carry at once. This is measured in "bits." A bit is the smallest piece of information a computer understands. If a bus is 8 bits wide, it can send 8 bits of information at the same time. A 64-bit bus can send 64 bits at once, which is much faster!
Common bus sizes include:
- 4 bits
- 8 bits
- 16 bits
- 32 bits
- 64 bits
- 128 bits
The wider the bus, the more data it can move at the same time. This makes your computer faster and more efficient.
What Does a Bus Connect?
Buses connect many important parts inside your computer. They help these parts work together smoothly. Here are some examples:
- The CPU (Central Processing Unit) to the computer's memory. The CPU is like the computer's brain. It needs to quickly get information from memory to do its work.
- Multiple CPUs in very powerful computers. This allows them to share tasks and work together.
- The ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit) to the rest of the CPU. The ALU is the part of the CPU that does all the math and logic problems.
- Storage devices like hard drives to the main system. This allows your computer to save and load files.
- Graphics cards to the main system. Graphics cards help your computer show images and videos on your screen.
- Other peripheral devices like printers or webcams.
Types of Computer Buses
There are different types of buses, each designed for specific tasks.
Internal Buses
These buses connect parts inside the computer's main circuit board, called the motherboard. They are very fast because they carry information over short distances. An example is the bus that connects the CPU to the RAM (memory).
External Buses
These buses connect your computer to devices outside of it. They are often slower than internal buses but are very useful for connecting many different types of devices.
Connecting Storage Devices
- Serial ATA (SATA) is a common bus used to connect modern hard drives and SSDs (Solid State Drives). It's very fast for moving large files.
- Parallel ATA (PATA or ATAPI) was an older type of bus used for hard drives. SATA replaced it because it's faster and uses fewer wires.
Connecting Other Devices
- USB (Universal Serial Bus) is a very popular external bus. You use it to connect many devices like keyboards, mice, printers, and phones. It's easy to use and can connect many different things.
- Firewire (also known as IEEE 1394) is another external bus. It's often used for connecting video cameras and other devices that need to transfer lots of data quickly.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Bus (informática) para niños
In Spanish: Bus (informática) para niños