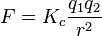Coulomb's law facts for kids
Coulomb's law is a rule discovered in the 1780s by a scientist named Charles-Augustin de Coulomb. It helps us understand how strong the push or pull is between two electric charges that are not moving. When electric charges are still, we call them electrostatic charges.
Contents
How Electric Charges Push or Pull Each Other
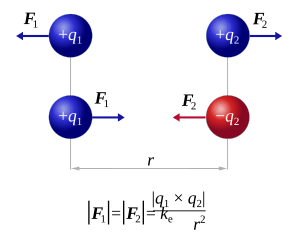
Imagine two tiny electric charges in empty space. If one charge is positive (+) and the other is negative (-), they will pull towards each other. This is called attraction.
But if both charges are the same, like both positive (+) or both negative (-), they will push away from each other. This is called repulsion.
This is similar to how magnets work. A North pole and a South pole attract each other. But two North poles or two South poles will push each other away.
Electric charges create an invisible area around them called an electric field. When two electric fields are in the same space, they put a force on each other. This force is known as 'Coulomb's force' or the electrostatic force. Coulomb's law tells us exactly how strong this force will be.
How Strong is the Force?
Coulomb's law helps us figure out the strength of the electrostatic force between two electric charges. The formula for this force looks like this:
Let's break down what these letters mean:
- F is the strength of the electrostatic force.
- q1 and q2 are the sizes of the two electric charges.
- r is the distance between the two electric charges.
- Kc is a special number that always stays the same. It's called the Coulomb's force constant.
This formula tells us a few important things:
- If the sizes of the charges (q1 and q2) get bigger, the electrostatic force (F) also gets stronger.
- If the distance (r) between the charges gets bigger, the electrostatic force (F) gets weaker. It gets weaker very quickly because the distance is squared (r²).
The exact value of the Coulomb's force constant (Kc) is about 9,000,000,000 (9 billion) Newtons meters2 per Coulomb2.
The Inverse-Square Law
The way the force gets weaker as the distance increases follows something called the Inverse-square law. This law means that if you double the distance between the charges, the force becomes four times weaker (because 2 squared is 4). If you triple the distance, the force becomes nine times weaker (because 3 squared is 9).
Many other things in nature follow this law too, like gravity, light, and how loud a sound is.
Related pages
- Coulomb, the unit for electric charge, named after Charles-Augustin de Coulomb.
- Inverse-square law, a rule that shows how strength changes with distance.
- Electrostatics, the study of electric charges that are not moving.
- Magnetic
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Ley de Coulomb para niños
In Spanish: Ley de Coulomb para niños