Desmosome facts for kids
A desmosome is like a tiny, strong spot-weld that helps cells stick together. Imagine your body's cells as bricks in a wall; desmosomes are the strong cement spots that hold those bricks tightly in place. They are found on the outer edges of a cell's plasma membrane, which is the protective skin around each cell.
Desmosomes are super important because they help cells form strong sheets, especially in tissues that need to withstand a lot of pulling and stretching. They make sure cells don't easily pull apart.
Contents
What are Desmosomes and How Do They Work?
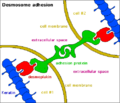
Desmosomes are special structures that link cells together. Think of them as a two-part connector. Each cell contributes one half of the connector, and these halves then join in the space between the cells.
The Parts of a Desmosome
A desmosome has three main parts:
- Plaques: Inside each cell, right under the cell membrane, there are thick, disc-shaped areas called plaques. These plaques are made of strong proteins.
- Connecting Proteins: Sticking out from these plaques, through the cell membrane, are special proteins called cadherins. These cadherins reach across the tiny gap between two cells and link up with cadherins from the neighboring cell. They act like tiny hooks or zippers, holding the cells together.
- Intermediate Filaments: Attached to the plaques inside the cell are strong, rope-like structures called intermediate filaments. These filaments spread out into the cell's internal framework, called the cytoskeleton. This connection makes the desmosome very strong, distributing any pulling force across the entire cell, not just at the spot where the cells are joined.
How Desmosomes Keep Cells Together
When two cells need to stick together, their desmosomes line up. The connecting proteins (cadherins) from one cell link with those from the other cell. At the same time, the intermediate filaments inside each cell are anchored to the plaques. This creates a continuous, strong connection from the inside of one cell, across the gap, to the inside of the next cell. This strong link prevents cells from tearing apart when your tissues are stretched or squeezed.
Where are Desmosomes Found in Your Body?
Desmosomes are especially common in tissues that experience a lot of mechanical stress. The most common place to find them is in epithelial tissue.
Desmosomes in Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial tissue forms protective layers and linings throughout your body. For example, your skin is made of epithelial cells. These cells are constantly exposed to friction and pressure. Desmosomes are abundant in your skin, helping the cells stay tightly connected to form a strong, protective barrier. Without them, your skin would easily tear.
Desmosomes in Other Tissues
You can also find desmosomes in other places where strong cell-to-cell adhesion is needed:
- Heart Muscle: The cells in your heart muscle (cardiac muscle) also have many desmosomes. This is crucial because your heart is constantly contracting and relaxing, and its cells need to stay firmly attached to each other to pump blood effectively.
- Other Organs: Desmosomes are present in various other organs and tissues where cells need to maintain their structure and function under stress.
Why are Desmosomes Important for Your Health?
Desmosomes are vital for keeping your body's tissues strong and healthy. If desmosomes don't work correctly, it can lead to health problems.
For example, certain skin conditions can happen if the proteins that make up desmosomes are faulty or attacked by the body's own immune system. When desmosomes are weak, the cells in the skin can separate, leading to blisters or fragile skin. Similarly, problems with desmosomes in the heart can affect how heart muscle cells stick together, potentially leading to heart conditions.
In summary, desmosomes are tiny but mighty structures that act as essential "spot-welds" between cells, ensuring the strength and integrity of your tissues, especially in places like your skin and heart.
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Desmosoma para niños
In Spanish: Desmosoma para niños