Economic sector facts for kids
India's economy is like a giant machine with many different parts working together. These parts are called economic sectors. They help us understand how people earn money and what kinds of jobs they do.
India is one of the fastest-growing large economies in the world. In 2017, it became the sixth-largest economy. Experts believe India will continue to grow, with its economy expected to expand by about 7.5% in the 2019-2020 financial year. This growth is helped by a large population and many young people ready to work.
Contents
Understanding Economic Sectors
Economic activities are all the ways people produce goods and services. We group these activities into different sectors based on what they do. In the past, most people worked in the primary sector. As societies grew, people needed more products, which led to the secondary sector developing. Later, a support system was needed for industries, leading to the tertiary sector.
Primary Sector: Getting Raw Materials
The primary sector involves activities that directly use natural resources. Think of jobs like:
- Farming (agriculture)
- Mining (digging for minerals)
- Fishing
- Forestry (managing forests)
- Dairy farming (producing milk)
This sector is called "primary" because it provides the basic materials for everything else. Since many natural products come from farming and related activities, it's also known as the Agriculture and allied sector. People who work in the primary sector are sometimes called red-collar workers because their jobs are often outdoors.
Secondary Sector: Making Things
The secondary sector takes the raw materials from the primary sector and turns them into finished products. This includes industries that manufacture goods. Examples of activities in this sector are:
- Making cotton fabric from raw cotton
- Producing sugar from sugarcane
- Building cars
- Processing food
- Refining oil
Because this sector involves many different types of industries, it's also called the industrial sector or manufacturing sector. People working in the secondary sector are often called blue-collar workers. Some important industries in India, often called Core Industries, include:
- Electricity
- Steel
- Refinery products (like petrol)
- Crude oil
- Coal
- Cement
- Natural gas
- Fertilizers
Tertiary Sector: Providing Services
The tertiary sector helps the primary and secondary sectors develop. It doesn't produce goods itself, but it provides support and services. Examples include:
- Transporting goods by trucks or trains
- Banking and insurance services
- Finance (managing money)
- Teaching
- Healthcare
This sector adds value to products and helps them reach customers. Jobs in this sector are often called white-collar jobs. A pink-collar worker is a term for someone in a job traditionally done by women, like a babysitter, florist, or nurse. These jobs might not require as much formal training as some white-collar jobs and historically had less pay or prestige.
Sunrise and Sunset Industries
A sunrise industry is a new sector that is growing very fast and shows a lot of promise for the future. It often has high growth rates and new ideas. Examples of sunrise sectors in India include:
- Information Technology (IT)
- Telecom (mobile phones, internet)
- Healthcare
- Retail (shops and shopping)
- Food Processing
- Fisheries
On the other hand, a sunset industry is one that is declining and has dim long-term prospects.
Why India Focused on Services
Normally, a country's economy moves from farming to industry, and then to services. However, India jumped from being mainly an agricultural economy to a service economy. India has become very successful in exporting software and IT-enabled services. This happened because India has many well-educated people who speak English, and labor costs are lower. The manufacturing sector (secondary sector) in India grew slower due to several reasons, such as:
- Old rules that made it hard for businesses to grow
- Limits on foreign investment
- Lack of support for private industries
- Power shortages
- Strict labor laws
- Not enough skilled workers
- Delays in getting land and environmental approvals
- Cheap imported goods
Quaternary Activities: The Knowledge Sector
The quaternary sector is a specialized part of the service sector. It focuses on knowledge and information. This includes jobs like:
- People working in offices
- Teachers in schools and universities
- Doctors and hospital staff
- Accountants and financial advisors
These activities help people innovate and improve services.
Quinary Activities: Top-Level Decisions
The quinary sector is where the highest-level decisions are made. This includes:
- Government officials who create laws
- Top leaders in businesses and industries
- Research scientists
- Financial and legal consultants
These jobs involve creating new ideas, interpreting data, and evaluating new technologies. People in these roles are sometimes called gold-collar professions because they have special and highly paid skills.
Organised and Unorganised Sectors
We can also divide the economy based on how jobs are structured.
Organised Sector
In the organised sector, jobs have fixed terms and regular working conditions. Employees get assured work and social security benefits. Businesses in this sector are registered with the government and follow specific laws. Examples include schools and hospitals. Workers in this sector have job security and fixed working hours. If they work extra, they get paid overtime.
Unorganised Sector
The unorganised sector includes workers who are self-employed or work for wages in small, unregistered businesses. These jobs are often casual or seasonal. This sector is known for:
- Low incomes
- Unstable and irregular employment
- Lack of protection from laws or trade unions
Workers in this sector are often spread out, making it hard to enforce laws that protect them. Even though it's unorganised, this sector contributes a lot to India's national income.
Public and Private Sectors
Another way to classify the economy is by ownership.
The Public Sector
In the public sector, the government owns most of the assets and provides various services. The main goal is not just to earn profits, but to serve the public. The government collects money through taxes to pay for these services. In India, some government-owned companies are called Central Public Sector Enterprises (CPSEs). They are classified into categories like Maharatna, Navratna, and Miniratna, based on their size and performance. These classifications give them more freedom to operate and grow.
The Private Sector
In the private sector, individuals or private companies own the assets and provide services. Their main goal is to earn profits. When you pay money for services like a taxi ride or a meal at a restaurant, you are usually paying a private individual or company.
Public Private Partnership (PPP)
A Public Private Partnership (PPP) is when the government and a private company work together to provide public services or build public assets (like roads or bridges). In a PPP, the private company invests money for a certain period. The government still has the main responsibility for providing the service. This arrangement helps when the government needs expert help or faces limits on borrowing money for big projects.
How Sectors Contribute to India's Economy
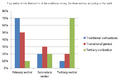
The services sector is the largest part of India's economy. In 2018-19, it contributed about 54.40% of India's total economic output. The industry sector (secondary sector) contributed about 29.73%. The agriculture and allied sector (primary sector) contributed about 15.87%. Even though agriculture contributes less to the total economic output, it still employs the largest number of people, nearly 53% of the workforce. The services sector employs about 29% and the secondary sector about 18%.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Sector económico para niños
In Spanish: Sector económico para niños