Ehlers–Danlos syndrome facts for kids
Ehlers–Danlos syndrome (EDS) is a rare condition that affects your body's connective tissue. Connective tissue is like the "glue" that holds your body together. It gives strength and flexibility to your skin, joints, blood vessels, and organs. People with EDS have a problem with this "glue," often because of a faulty protein called collagen. There is no cure for EDS, but doctors can help manage the symptoms.
Contents
What is Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome?
Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, or EDS, is a group of conditions that you are born with. It happens when your body doesn't make connective tissue correctly. This tissue is found all over your body. It supports your skin, bones, blood vessels, and many organs.
What Are the Symptoms of EDS?
The symptoms of EDS can be different for each person. Some common signs include:
- Stretchy skin: Your skin might feel very soft and can stretch more than usual.
- Flexible joints: You might be "double-jointed," meaning your joints can bend further than most people's. This can sometimes lead to joints easily slipping out of place.
- Joint pain: Many people with EDS experience pain in their joints.
- Flat feet: Your feet might be flatter than average.
- Early arthritis: Some people develop arthritis at a younger age.
More serious types of EDS can affect blood vessels or even major organs.
Different Types of Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome
There are several types of EDS, and each one affects the body in slightly different ways. The main types are:
- Hypermobility EDS (hEDS): This is the most common type. It mainly causes very flexible joints and joint pain.
- Classical EDS (cEDS): This type often causes very stretchy skin that bruises easily. It can also lead to scars that look thin and wide.
- Vascular EDS (vEDS): This is a more serious type. It can affect blood vessels and internal organs, making them fragile.
- Kyphoscoliosis EDS (kEDS): This type can cause a curve in the spine (scoliosis). It also makes joints very loose and muscles weak.
- Arthrochalasia EDS (aEDS): People with this type have very loose joints, especially at birth.
- Dermatosparaxis EDS (dEDS): This type causes extremely fragile and saggy skin.
Images for kids
-
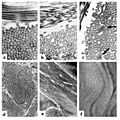
The collagen fibril and EDS: (a) Normal collagen fibrils are of uniform size and spacing. Fibrils from a person with dermatosparaxis (b) show dramatic alterations in fibril morphology with severe effects on the tensile strength of connective tissues. A person with classical EDS (c) shows composite fibrils. Fibrils from a TNX-deficient person (d) are uniform in size and no composite fibrils are seen. TNX-null (e) fibrils are less densely packed and not as well aligned to neighboring fibrils.
-
Individual with EDS displaying hypermobile metacarpophalangeal joints
See also
 In Spanish: Síndromes de Ehlers-Danlos para niños
In Spanish: Síndromes de Ehlers-Danlos para niños