Felipe González de Ahedo facts for kids
Felipe González de Ahedo was a Spanish navigator and mapmaker. He is famous for claiming Easter Island for Spain in 1770. He was born on May 13, 1714, in Santoña, Spain, and passed away on October 26, 1802.
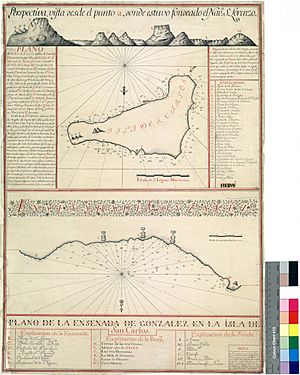
In 1770, González de Ahedo led two Spanish ships, the San Lorenzo and the Santa Rosalia. They were sent by the Viceroy of Peru, Manuel de Amat y Juniet, who was like a governor for the King of Spain. They arrived at Easter Island on November 15, 1770. This was only the second time Europeans had ever seen the island!
They stayed for five days, carefully exploring the coast. They named the island Isla de San Carlos and officially claimed it for King Charles III of Spain. They even signed an agreement with the islanders and put up three wooden crosses on three small hills on Poike volcano. The Spanish sailors were amazed by the huge stone statues, called moai, which were all standing upright at that time.
Contents
Early Life and Dreams
Felipe González de Ahedo was born in Santoña, a small town in Spain, around 1714. His parents were respected people, but they didn't have a lot of money. Even so, they supported Felipe's dream of becoming a sailor. Since he grew up right by the sea, he loved the ocean from a young age. This love led him to choose a life at sea.
Starting a Career at Sea
When Felipe was 25, he began his career in the Royal Spanish Navy. He started as an apprentice on a ship called the San Bernardo. Just two years later, he was assigned to the Santiago. On this ship, he became known as a very skilled sailor. His leaders noticed his talent.
Exciting Adventures
In 1730, Felipe joined the ship Aranzasu. On this journey, he traveled to the West Indies and back. This was his first big adventure in the New World. By 1736, Felipe was on a new ship called the Incendio. He sailed on it to Veracruz, which was his first time in Central America. After several more years of service, Felipe was promoted to junior lieutenant in 1751.
In 1760, Felipe was given command of a fast warship called a frigate, named the Arrogant. His job was to protect eighteen other ships hiding in the Bay of Ferrol from enemy attacks. After this, Felipe served on many different ships until 1766. That year, he was promoted to Commander of the Firme. He used the Firme to hunt down "piratical xebeques of Algiers." Xebeques were Mediterranean sailing ships, often used for trading. Felipe saw many of these pirate ships, but his ship wasn't fast enough to catch any of them.
Claiming Easter Island
In 1769, Felipe was put in charge of the San Lorenzo. This was a very impressive ship with space for 64 cannons. Ahedo sailed this ship to "El Callao de Lima" in Peru, carrying soldiers and military supplies. His journey took over six months, and he arrived in 1770.
Once he reached El Callao de Lima, the Viceroy told Felipe to claim Easter Island for Spain. Spain wanted to own the island. After returning from Easter Island, having successfully claimed it, Felipe was promoted again to Post Captain by the officials in El Callao de Lima.
Later Life and Retirement
By 1772, Felipe had returned to Spain. He exchanged his valuable items for money, getting 119,521 pesos. This finally brought wealth to his family. In 1774, Felipe traveled to El Callao de Lima once more. In 1778, the king himself assigned him to the ship San Isidoro.
By 1782, Felipe had been promoted to a Commodore. He served on the ship San Eugenio. This was the last ship he would ever serve on. After his time with the San Eugenio, he stopped active service at sea. However, he continued to work in the Navy Office until he passed away in 1802. Felipe González de Ahedo was around 88 years old and had spent about 63 of those years serving at sea.
 In Spanish: Felipe González Ahedo para niños
In Spanish: Felipe González Ahedo para niños