Glass transition facts for kids
The glass transition is a special change that happens to some solid materials. Imagine a hard, brittle material, like a piece of plastic or glass. When you heat it up, it doesn't melt right away like ice turning into water. Instead, it slowly becomes soft and rubbery. This change from hard to soft is called the glass transition. A solid that can do this is often called a glass.
When a thick, gooey liquid cools down very quickly without forming crystals, it can become a glass. This process is called vitrification. Think of how glass is made: hot, liquid glass cools fast to become a solid, but its atoms aren't neatly lined up like in a crystal.
Contents
What is Glass Transition Temperature?
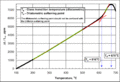
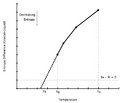
The glass transition temperature (often written as Tg) is the exact temperature where this change happens. It's like a magic number for these materials.
- If a material is below its Tg, it feels hard and stiff, like a normal plastic toy.
- If it's above its Tg, it becomes soft and flexible, almost like rubber.
This Tg is always lower than the material's actual melting temperature (Tm), which is when it would turn into a true liquid. Some plastics, called thermosets, don't melt at all. They just burn if you heat them too much. But even these can go through a glass transition, becoming softer before they burn.
Everyday Examples of Glass Transition
You see the glass transition in action all the time!
- Ironing clothes: When you iron clothes, you heat the fabric. The fibers in the fabric (which are often polymers) go through their glass transition. They become soft and flexible, allowing you to smooth out wrinkles. As they cool, they become stiff again, holding the new shape.
- Plastic bottles: A plastic bottle is hard and rigid at room temperature. If you heat it slightly (but not enough to melt it), it can become soft and easy to reshape. This is because it has passed its glass transition temperature.
- Rubber bands: A rubber band is already above its glass transition temperature at room temperature, which is why it's stretchy and flexible. If you cooled it down a lot, it would become hard and brittle.
Understanding the glass transition helps scientists and engineers create new materials with specific properties, like plastics that are tough for packaging or flexible for clothing.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Transición Vítrea para niños
In Spanish: Transición Vítrea para niños