Graphical projection facts for kids
A graphical projection is a way to show a three-dimensional object on a flat surface, like a piece of paper or a computer screen. Think of it like taking a picture of something real and making it fit onto a flat photo. It helps us see depth and shape even when we're looking at a 2D image.
Contents
What is Graphical Projection?
Graphical projection is all about making 3D objects look real on a 2D surface. Imagine you are drawing a cube. If you just draw a square, it looks flat. But if you use graphical projection, you can make it look like a real cube with sides and corners that go back into space.
Why Do We Use Projections?
We use projections in many places!
- Art and Drawing: Artists use it to create realistic paintings and drawings.
- Architecture: Architects use it to design buildings and show clients what they will look like.
- Video Games: Game designers use it to make 3D worlds appear on your screen.
- Engineering: Engineers use it to design parts and machines.
It's a super important tool for anyone who needs to show 3D things on a flat surface.
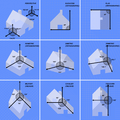
Types of Graphical Projections
There are two main types of graphical projections:
- Parallel Projection
- Perspective Projection
Let's look at how they are different.
Parallel Projection
In parallel projection, all the lines that are parallel in the real 3D object stay parallel in the drawing. This means that objects don't get smaller as they get further away. It's like looking at something with a very, very powerful zoom lens from far away.
Orthographic Projection
One common type of parallel projection is orthographic projection. This is like looking straight at one side of an object.
- Top View: You see the object from directly above.
- Front View: You see the object from directly in front.
- Side View: You see the object from directly to the side.
Engineers and architects often use orthographic projections. This is because they show the true size and shape of each side. It makes it easy to measure things accurately.
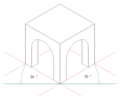
Axonometric Projection
Another type of parallel projection is axonometric projection. This shows the object from an angle. It gives you a better idea of the object's overall shape.
- Isometric Projection: This is a very popular type. All three axes (length, width, height) are equally scaled. It makes objects look balanced and easy to understand.
- Dimetric Projection: Two of the three axes are scaled equally.
- Trimetric Projection: All three axes are scaled differently.
Oblique Projection
In oblique projection, one face of the object is drawn flat, facing you. The other sides are drawn at an angle. This can make the front of the object look very clear.
- Cavalier Projection: The lines going back into space are drawn at full scale.
- Cabinet Projection: The lines going back into space are drawn at half scale. This makes the object look more realistic.
Perspective Projection
Perspective projection is how our eyes see the world. In this type of projection, objects that are further away appear smaller. Parallel lines seem to meet at a single point in the distance, called a vanishing point. This makes the drawing look very realistic and natural.
One-Point Perspective
In one-point perspective, you look straight at one face of the object. All lines that go away from you meet at a single vanishing point on the horizon line. This is great for drawing roads, hallways, or buildings seen from the front.
Two-Point Perspective
Two-point perspective is used when you look at an object from an angle. You will see two sides of the object, and lines from each side will go to two different vanishing points on the horizon. This is often used for drawing buildings from a corner.
Three-Point Perspective
Three-point perspective adds a third vanishing point. This point is either above or below the horizon line. It's used when you are looking at an object from a very high or very low angle. This makes the object look even more dramatic, like looking up at a tall skyscraper or down from an airplane.
How Projections Are Used Today
Graphical projections are still very important.
- Computer Graphics: When you play a video game, the 3D world you see is created using perspective projection. The computer calculates how everything should look from your character's viewpoint.
- Animation: Animators use projections to make characters and scenes move realistically.
- Virtual Reality (VR): VR headsets use advanced projections to create immersive 3D environments that feel like you are really there.
Understanding graphical projection helps us appreciate how artists, designers, and computer programmers create the amazing visual worlds we see every day!
Images for kids
-
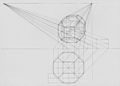
Axonometric projection of a scheme displaying the relevant elements of a vertical picture plane perspective. The standing point (P.S.) is located on the ground plane π, and the point of view (P.V.) is right above it. P.P. is its projection on the picture plane α. L.O. and L.T. are the horizon and the ground lines (linea d'orizzonte and linea di terra). The bold lines s and q lie on π, and intercept α at Ts and Tq respectively. The parallel lines through P.V. (in red) intercept L.O. in the vanishing points Fs and Fq: thus one can draw the projections s′ and q′, and hence also their intersection R′ on R.
See also
 In Spanish: Proyección tridimensional para niños
In Spanish: Proyección tridimensional para niños
 | Janet Taylor Pickett |
 | Synthia Saint James |
 | Howardena Pindell |
 | Faith Ringgold |