Ground tissue facts for kids
Have you ever wondered what makes up most of a plant? It's not just the leaves, stems, or roots you see! Inside, plants have special parts called tissues. Think of tissues like different teams of cells working together. Ground tissue is the name for the main bulk of a plant. It's like the "filler" or "stuffing" that makes up most of the plant's body, not including its outer skin or the tubes that carry water and food.
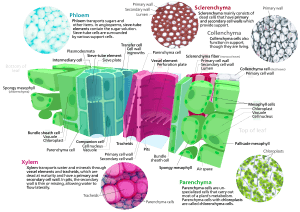
Ground tissue helps plants do many important jobs. These jobs include making food (like in leaves), storing water and nutrients, and giving the plant strength and support. Scientists usually sort ground tissue into three main types. They look closely at the cell walls of the cells to tell them apart.
Contents
What are the Main Types of Ground Tissue?
Plants have three main kinds of ground tissue. Each type has cells with different kinds of cell walls, which helps them do their specific jobs.
Parenchyma: The All-Rounder Cells
Parenchyma cells are like the general-purpose workers of the plant world. They are the most common type of plant cell.
- Thin Walls: These cells have thin, flexible primary walls.
- Stay Alive: Most parenchyma cells stay alive even after they are fully grown.
- Many Jobs: They form the soft parts of plants, like the juicy inside of fruits or the main part of leaves. Parenchyma cells are super important for:
* Making food through photosynthesis (using sunlight to make energy). * Storing food (like starch) and water. * Helping with healing and repair if a plant gets damaged.
Collenchyma: Flexible Support for New Growth
Collenchyma cells are like the flexible support beams for a plant. They help keep the plant upright without being too stiff.
- Unevenly Thick Walls: These cells have primary walls that are thicker in some spots than others. This makes them strong but still bendy.
- Stay Alive: Collenchyma cells also stay alive when they are mature.
- Support New Parts: They provide extra support, especially in parts of the plant that are still growing, like young stems and leaf stalks. This allows the plant to grow taller and wider without breaking.
Sclerenchyma: Strong and Stiff Support
Sclerenchyma cells are the main support system for a plant, like the steel beams in a building. They give plants their hardness and stiffness.
- Thick, Hard Walls: These cells have very thick and strong secondary walls. These walls are often made hard by a substance called lignin, which is what makes wood so tough.
- Often Die: Sclerenchyma cells often die once they are fully grown, leaving behind their strong cell walls to provide support.
- Main Support: They provide the main structural support to a plant. You can find them in hard parts like the shells of nuts, the gritty texture in pears, or the strong fibers in plant stems.
Images for kids
 | Emma Amos |
 | Edward Mitchell Bannister |
 | Larry D. Alexander |
 | Ernie Barnes |