Haemophilia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Haemophilia |
|
|---|---|
A drawing of clotting factor VIII
|
|
| Classification and external resources | |
| Synonyms | Hemophilia |
| Specialty | Haematology |
| Patient UK | Haemophilia |
Haemophilia (also spelled hemophilia) is a mostly inherited genetic disorder. It affects how the body makes blood clots. Clotting is the process that stops bleeding after a cut or injury. People with haemophilia bleed for a longer time than usual because their blood does not have enough "clotting factors." These factors are proteins that act like glue to stop bleeding.
This condition can cause easy bruising and bleeding inside the body, especially in the knees, ankles, and elbows. It can also affect the brain. People with a mild case might only have problems after a big accident or surgery.
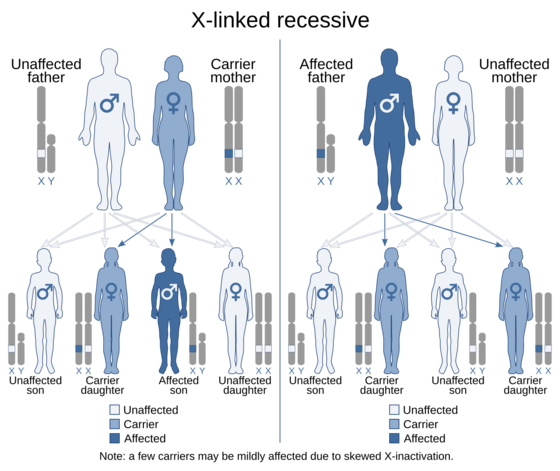
There are two main types. Haemophilia A is caused by missing clotting factor VIII. Haemophilia B is caused by missing clotting factor IX. The condition is usually passed down from parents to children through genes on the X chromosome. It mostly affects boys. Girls can be carriers, meaning they have the gene but usually do not get sick. Sometimes, a new mutation happens, and a child is born with it even if their parents do not have the gene.
Doctors diagnose haemophilia by testing the blood. Treatment involves replacing the missing clotting factors. This is done by injecting medicine into a vein. In recent years, new treatments like gene therapy have been approved to help the body make its own clotting factors.
Contents
Signs and symptoms
The main sign of haemophilia is bleeding that does not stop easily. The symptoms depend on how severe the condition is.
External and Internal Bleeding
People with severe haemophilia may have bleeding episodes called "bleeds." These can happen for no clear reason.
- External bleeding: This happens from cuts, scratches, or nosebleeds. It takes a long time for the bleeding to stop.
- Internal bleeding: This happens inside the body. It is common in severe cases.
Joint Problems
A very common symptom is bleeding into the joints, such as the knees and elbows. This is called hemarthrosis. It can cause:
- Swelling
- Pain
- Tightness in the joint
If this happens often, it can damage the joints permanently. This can make it hard to walk or move the arms.
Other Signs
- Large, deep bruises.
- Bleeding after dental work or losing a tooth.
- Blood in urine.
- In babies, signs might be seen after medical procedures done at birth or when they start crawling and get bumps.
Emergency Signs
Bleeding inside the skull is a medical emergency. It can happen after a head injury. Signs include bad headaches, vomiting, sleepiness, or confusion. This requires immediate help from a doctor.
Genetics and Inheritance
Haemophilia is a genetic condition. This means it is caused by instructions in a person's DNA. These instructions are found on chromosomes.
How it is Passed Down
The genes for making clotting factors are on the X chromosome.
- Females have two X chromosomes (XX). If one has the faulty gene, the other healthy X chromosome can usually do the work. Females are often "carriers." They can pass the gene to their children but usually do not have symptoms themselves.
- Males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY). If a boy inherits the faulty X chromosome from his mother, he will have haemophilia because he does not have a second X chromosome to help.
Family Patterns
- If a mother is a carrier, there is a 50% chance her son will have haemophilia. There is a 50% chance her daughter will be a carrier.
- If a father has haemophilia, he cannot pass it to his sons. However, all his daughters will be carriers.
About one-third of cases happen by accident (spontaneous mutation) when a baby is forming. This means a child can be born with haemophilia even if no one else in the family has it.
Diagnosis
Doctors can find out if a person has haemophilia through blood tests.
Testing
- Before birth: If a family knows they have a history of haemophilia, doctors can test the baby during pregnancy.
- After birth: Doctors test the blood from the umbilical cord or a vein. The test measures how long it takes for blood to clot and checks the levels of clotting factors.
Types
Tests show which type of haemophilia a person has:
- Haemophilia A: Low levels of Factor VIII. This is the most common type.
- Haemophilia B: Low levels of Factor IX.
- Haemophilia C: Low levels of Factor XI. This is rare and milder.
Treatment and Management
There is no cure that fixes the genes permanently for everyone yet, but treatments are very effective. The main goal is to replace the missing clotting factor so the blood can clot.
Replacement Therapy
People take medicine that contains the missing clotting factor. This is usually a white powder mixed with water and injected into a vein.
- On-demand: Taking medicine only when bleeding happens.
- Prophylaxis (Preventive): Taking medicine regularly (like 2 or 3 times a week) to prevent bleeding before it starts. This helps protect joints.
The clotting factors can be made from donated human plasma or created in a lab (recombinant). Lab-made factors are safer because they do not carry viruses.
New Medicines
Scientists have developed new ways to treat the disease:
- Desmopressin (DDAVP): A medicine for mild haemophilia A. It helps the body release its own stored clotting factor.
- Gene Therapy: This is a new treatment. It puts a working gene into the body so the liver can make clotting factors.
- In November 2022, the FDA approved Hemgenix for Haemophilia B.
- In June 2023, Roctavian was approved for Haemophilia A.
- In March 2025, Fitusiran (Qfitlia) was approved in the United States.
Safety and Lifestyle
People with haemophilia need to be careful with certain activities.
- Avoid: Contact sports like American football, boxing, and hockey because of the risk of injury.
- Recommended: Swimming, walking, and golf are safe exercises.
- Medicine Safety: They should not take medicines that thin the blood, like aspirin or ibuprofen. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) is usually safe for pain.
History
Haemophilia has been known for a long time. Ancient writings mentioned boys who bled too much after minor surgeries.
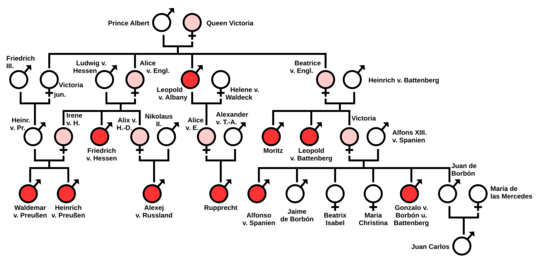
The Royal Disease
Haemophilia is often called "the royal disease." Queen Victoria of the United Kingdom was a carrier of Haemophilia B. She passed the gene to several of her children.
- Her son Leopold had the disease.
- Her daughters Alice and Beatrice were carriers.
Through her children, the disease spread to the royal families of Spain, Germany, and Russia. The most famous case was Tsarevich Alexei of Russia. He was the son of Tsar Nicholas II. His illness was a secret and led his mother to trust the mystic Grigori Rasputin, who claimed he could heal the boy.
Blood Safety History

In the 1980s, the medicine used to treat haemophilia was made from donated blood. At that time, doctors did not know how to screen blood for certain viruses. Many people with haemophilia became very sick with HIV and Hepatitis C because of contaminated medicine.
Since then, safety has improved greatly. Today, blood is carefully tested, and most medicines are made in labs without using human blood, making them very safe.
See also
 In Spanish: Hemofilia para niños
In Spanish: Hemofilia para niños
- Nicholas II of Russia
- Coagulopathy
- Von Willebrand disease
- World Federation of Hemophilia