Hand, foot and mouth disease facts for kids
Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD) is a common illness. It is caused by a tiny germ called a virus. Specifically, a type of virus called Coxsackie A. This disease mostly affects babies and young children. It spreads easily from one person to another. This is why it often shows up in places like daycares or schools. Most people who get HFMD don't need to go to the hospital. The good news is there's no special medicine needed. It usually gets better on its own in about one or two weeks.
Contents
What are the Symptoms of HFMD?
When someone has Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease, they might feel a few different things. The symptoms can be mild or a bit more noticeable. Here are some common signs:
- Fever (when your body gets too hot)
- Headache
- Feeling sick to your stomach (vomiting)
- Feeling very tired (fatigue)
- General aches and pains
- Earache
- Sore throat
- Painful sores inside the mouth
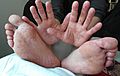
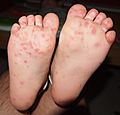
- A rash on the body
- Sores with small blisters on hands and feet
- Trouble eating because of mouth sores
- Diarrhea (loose stools)
How HFMD Spreads and How it's Treated
HFMD is very common, especially among younger kids. It spreads easily from person to person. This often happens in places where children are close together. Think of nurseries or kindergartens. The virus can spread through coughing, sneezing, or contact with fluids from blisters. It can also spread through poop from an infected person.
Most people who get HFMD don't get very sick. Only a small number might need to go to a hospital. There is no specific medicine to cure HFMD. It usually goes away by itself after one or two weeks. Doctors might suggest ways to help with the symptoms. This could include medicines for fever or pain. It's important to drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Enfermedad mano-pie-boca para niños
In Spanish: Enfermedad mano-pie-boca para niños