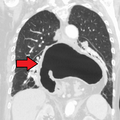
Hiatal hernia facts for kids
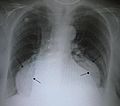
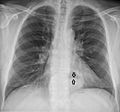
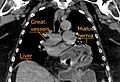
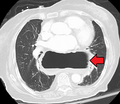
A hiatal hernia happens when part of your stomach or other organs in your belly move up into your chest. This happens through a small opening in your diaphragm, which is the muscle that separates your chest from your belly. When this happens, it can cause problems like heartburn or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), where stomach acid comes back up. You might also have trouble swallowing or feel chest pain. Sometimes, it can even lead to other issues like blocked intestines or low iron in your blood.
What Makes It Happen?
Some things can make a hiatal hernia more likely. Being very overweight and getting older are common reasons. Other things that can increase the risk include having a curved spine (called scoliosis), getting an injury, or having certain types of surgery.
Many people have hiatal hernias. In the United States, between 10% and 80% of people might have one, though not everyone has symptoms.
Feeling Better
If someone has symptoms from a hiatal hernia, there are ways to feel better. Losing weight can help. Changing how and when you eat, like eating smaller meals, can also make a difference. Raising the head of your bed while you sleep can help keep stomach acid down.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Hernia de hiato para niños
In Spanish: Hernia de hiato para niños