Home cinema facts for kids
A home cinema, also known as a home theater, is a fun audio and video system for your home. It tries to make you feel like you're at a real movie theater, but right in your own house! People use regular electronics like big TVs, projectors, and special sound systems to create this experience.
Back in the 1980s, home cinemas usually had movies on big discs called LaserDiscs or VHS tapes. You'd play them on a LaserDisc player or a VCR, and watch on a large TV. By the 2000s, technology got much better. Sound systems, video players, and TVs improved a lot. This meant clearer pictures and amazing sound. Now, many Blu-ray players can even stream movies and TV shows from the internet using services like Netflix. This means you don't have to go to a video store anymore!
Today, in the 2020s, a home cinema usually has a huge projected image or a large, flat, high-definition TV. It plays movies or other high-quality videos. The sound system often has many speakers, sometimes five or more, that create "surround sound." There's also usually a big speaker called a subwoofer. This speaker makes the deep rumbling sounds and bass from movie soundtracks really powerful.
Contents
Early Home Cinema Ideas
One of the very first ideas for a home theater was the Edison Home Projecting Kinetoscope, introduced in 1912. It used a special kind of film. This machine was quite expensive for its time, costing $175. It was also a bit tricky to use. Because of these reasons, it didn't become very popular. Production stopped after a big fire at Edison's factory in 1914.
Home theater systems continued to develop. In the 1920s, people started using 16mm film projectors. By the 1930s, smaller 8mm film and 16mm film with sound became available. In the 1950s, showing "home movies" became popular for many families in the United States. This was because Kodak 8mm film projectors became more affordable.
From the mid-1980s to the mid-1990s, a typical home cinema used a LaserDisc or VHS player. The movie would show on a large TV, often a rear-projection TV. The sound would come from a stereo system. Some people even used expensive projectors in dark rooms. Watching movies on VHS at home became a very popular hobby in the 1980s.
Starting in the late 1990s and through the 2000s, home theater technology really took off. This was thanks to DVDs, surround sound speaker systems, and high-definition televisions (HDTVs). At first, HDTVs were big and heavy, but then flat-screen TVs became common. The 2010s brought even better and more affordable large flat-screen HDTVs. High-resolution video projectors and Blu-ray discs also became popular.
Some studies suggest that movies feel more exciting when watched in a movie theater. However, the main reason people love home cinemas is how convenient they are. You can watch movies whenever you want, right at home!
What Makes a Home Cinema?
The term home cinema can mean many different systems for watching movies at home. The simplest and cheapest system might be a digital media player connected to a large TV. It could also include an affordable "home theater in a box" system with surround sound speakers and a subwoofer.
A more expensive setup might have a Blu-ray player, a special computer for movies (HTPC), or a streaming device. It could also feature an even bigger screen or a projector. These systems often have a powerful sound receiver with five or more surround-sound speakers and one or two strong subwoofers.
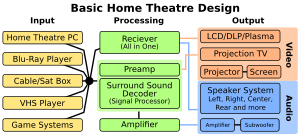
The way you design your home cinema is a personal choice. It depends on how much money you want to spend and how much space you have. Here are the basic things you need for a home theater:
- A large TV or a good quality video projector. This could be an LCD, DLP, Plasma, or OLED screen. It should be at least 27 inches (69 cm) measured diagonally.
- An AV receiver or a pre-amplifier and amplifier. This equipment handles the sound. It should be able to play at least stereo sound, but ideally 5.1 Channel Dolby Digital and DTS audio.
- Something to play or broadcast movies. This could be a DVD player, a Blu-ray disc player, a cable or satellite receiver, or a video game console.
- A set of speakers. You need at least two for stereo sound. Most systems have six to eight speakers with a subwoofer for deep bass sounds.
The most expensive home cinema setups can cost over $100,000! These are found in the homes of very wealthy people. They often have huge, high-resolution digital projectors and screens. Some even have custom-built rooms with cinema-style chairs and amazing sound equipment. These systems are designed to be as good as, or even better than, commercial movie theaters.
Designing Your Home Cinema
In the 2010s, many home cinema fans wanted to make their home setup feel just like a real movie theater. To do this, they bought better quality equipment than what's used for everyday TV watching. A typical home cinema includes these parts:
- Movies or other content: The main reason for a home cinema is to watch movies on a big screen. This makes vast landscapes or big battle scenes look much more impressive. As of 2016, people also watched TV shows, sports, or concerts on Blu-ray players. Many smart players can also stream movies and shows from the internet.
- Video and audio players: You need one or more devices to play your content. High-quality Blu-ray discs are often preferred. DVD players or video game consoles are also used. Some home theaters have a special computer (HTPC) to store movies and music.
- Sound and picture processing: The signals from your players go through an AV receiver or a sound processor. This device handles complex surround sound formats like Dolby Digital and DTS. You use it to choose what you want to watch, like a DVD or a streaming movie.
- Sound output: This includes amplifiers and speakers. You need at least two speakers for stereo sound. Most systems have a multi-channel amplifier and six or more speakers. A 5.1 surround sound system has front left and right speakers, a center speaker, rear left and right speakers, and a subwoofer for bass. Some people even have 7.1 surround sound or more!
- Picture output: This is usually a large, flat-screen HDTV. Some people might have a 3D TV. As of 2015, flat-screen HDTVs were very common. Options include LCD, plasma, and OLED TVs. Many home cinema users also prefer a video projector and a movie screen. The screen can be portable, permanently mounted, or even just a wall.
- Seating and feel: Comfortable seating makes the cinema experience better. Some fancy home cinemas have padded chairs just like in a movie theater. High-end home theaters often have special sound insulation to keep noise in. They might also have special wall treatments to make the sound inside the room perfect.
Buying Components or a Box Set?
You can set up a home cinema in two main ways. You can buy each part separately, like an amplifier from one company and speakers from another. Or, you can buy a "Home Theater in a Box" (HTIB) package. This package includes almost everything you need from one company, except for the TV or projector. HTIB systems usually come with a DVD or Blu-ray player, a surround sound amplifier, five surround speakers, a subwoofer, cables, and a remote.
Buying separate parts lets you get better quality video or audio. You can also choose parts that work best for your specific room. However, to buy individual parts, you need to know a lot about sound and video systems. For example, some speakers work better in small rooms, while others are for larger spaces. You also need to understand things like speaker power and how different devices connect.
Because buying separate parts can be tricky, HTIB systems are a simpler and often cheaper choice for many families. They are also great for smaller living spaces like apartments where noise might be a problem.
Special Home Cinema Rooms
Some people who really love home cinema build a special room in their house just for it. These advanced setups often have special sound designs. They might even have a "room-in-a-room" structure to block out sound and make the listening experience better. They usually have a very large screen, often using a high-definition projector. These rooms are sometimes called screening rooms to show they are more advanced than simpler setups.
In some very enthusiastic home cinemas, people try to make a small-scale movie theater. They might have a projector in its own booth, special cinema chairs, curtains in front of the screen, movie posters, or even a popcorn machine! More commonly, dedicated home theaters are a bit simpler but still very impressive.
As of 2016, very expensive home cinema systems (over $100,000) are becoming less common. This is because digital audio and video technology has improved so much. Prices have dropped quickly, making a great home cinema setup more affordable than ever. Now, many do-it-yourself enthusiasts can build a true digital home theater for much less money. Consumer-grade equipment can even meet some of the high standards of modern commercial cinemas.
Comfortable Seating
Home cinema seating includes chairs or sofas made especially for watching movies at home. Some seats have cup holders in the armrests and shared armrests between seats. Some look like real cinema chairs with flip-up cushions. Other systems have soft leather reclining chairs with footrests. You can even find seats with storage, snack trays, or special devices that let you feel the low bass sounds through the chair. Home cinema seating is usually much more comfortable than seats in a public movie theater.
Outdoor Cinema Fun
If you have a big enough backyard, you can even set up a home cinema outdoors! This could be a temporary setup with a foldable screen, a projector, and a couple of speakers. Or, it could be a permanent setup with a huge screen and a sound system in a weather-proof cabinet. Outdoor home cinemas are popular for BBQ parties and pool parties. Some companies even sell special outdoor cinema packages with inflatable movie screens. Some people have even created mobile "drive-in theaters" that can play movies in public spaces. These usually need a powerful projector, a laptop or DVD player, outdoor speakers, or an FM transmitter to send the sound to car radios.
History of Home Cinema
1920s–1940s
In the 1920s, the first home cinemas used silent 16mm film projectors. Later, in the 1930s, 8mm film and 16mm film with sound were introduced. These were very rare and expensive luxuries.
1950s–1970s
In the 1950s, home movies became more popular in the United States. Kodak 8mm film cameras and projectors became more affordable. People would project these small films onto a portable screen, often without sound. This was the first practical home theater. They were mostly used to show family videos, but sometimes also commercial films. Very wealthy people had "screening rooms" with 16mm or even 35mm projectors for showing commercial films.
Portable home cinemas got better with color film and sound, but they were still a bit awkward and costly. When home video came along in the late 1970s, it almost ended the market for 8mm film cameras. VCRs connected to regular TVs were much simpler and more flexible.
1980s
The 1980s brought new excitement to home cinema with multi-channel audio systems and LaserDisc players. The first known home cinema system was built in 1974 by Steve J. LaFontaine. He created a special sound room and used modified TVs to project images. In 1982, a public demonstration at a big electronics show in Chicago really kicked off the home cinema business. This demonstration showed how combining high-quality video with multi-channel surround sound could create an amazing home experience.
1990s
In the early to mid-1990s, a typical home cinema had a LaserDisc player or VHS VCR connected to a large screen. Rear projection TVs were common for more affordable setups. In the late 1990s, interest in home cinema grew even more. This was thanks to DVDs, Dolby Digital, and DTS 5.1-channel audio. High-quality front video projectors also became available, offering a cinema experience at a price similar to a big-screen HDTV.
2000s
In the 2000s, new technologies like high-definition video and Blu-ray discs made it even easier to enjoy a cinematic feeling at home for a lower price. Newer, high-quality audio formats like Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD Master Audio were introduced. Speaker systems with more audio channels (like 6.1, 7.1, and even more) also became available for an even better movie experience.
2010s
By the mid-2010s, Blu-ray discs were a common way to watch movies at home. Online streaming services like Netflix and YouTube also offered lots of high-definition content, including some 4K resolution videos. The first 4K Blu-ray discs came out in 2016. Around this time, 4K TVs and computer monitors became much cheaper and more common. High-definition video projectors also kept getting better and more affordable.
Because prices kept dropping, large TVs (up to 80 inches) became a good alternative to video projectors for living rooms. Technologies like local dimming improved the black levels on LCD screens, making them better for dark rooms. OLED TVs, which have even better black levels, started to appear in the second half of the decade.
2020s
As of 2020, video projectors were still the only good choice for screen sizes much larger than 80 inches.
Quality Standards for Equipment
There are special guidelines for how quiet a cinema or home cinema room should be. This is called Noise Criteria (NC). It measures the background noise level in a room at different sound frequencies. For example, for a theater to be THX-certified (a high-quality standard), it must have a background sound level of NC-30 or less. This helps you hear all the quiet and loud parts of the movie sound.
Here are some NC levels:
- NC 40: This is a noticeable but acceptable level of background noise. It's the highest level that is still considered okay.
- NC 30: This is a good NC level. It's needed for THX certification in cinemas.
- NC 20: This is an excellent NC level. It's hard to achieve in large rooms and is sought after for dedicated home cinema systems. For example, a home cinema needs an NC 22 rating to be THX-certified.
- NC 10: This noise level is almost impossible to achieve. It's as quiet as calm breathing.
Projectors used for home cinemas also have recommended qualities:
- Brightness: Usually at least 1800 lumens.
- Resolution: The number of pixels that make up the image. Usually at least 1920×1080, which is an HDTV standard.
- Contrast: How well white, black, and gray colors are shown. Usually a minimum of 5000:1.
- HDMI connections: These are common for connecting devices.
- Good quality manufacturers: This depends on what the user likes and how much they want to spend. For some, a well-known electronics brand is good quality. For others, a professional brand like Christie (used in commercial theaters) might be their choice.
More to Explore
- Digital cinema
- Home theater PC
- Media server
- Over-the-top media service
See also
 In Spanish: Cine hogareño para niños
In Spanish: Cine hogareño para niños
 | Frances Mary Albrier |
 | Whitney Young |
 | Muhammad Ali |