Leó Szilárd facts for kids
Leó Szilárd (born February 11, 1898 – died May 30, 1964) was a brilliant scientist and inventor. He was born in Hungary and later became an American citizen. Szilárd was a physicist, which means he studied how the universe works, from tiny atoms to giant galaxies.
He is famous for several big ideas that changed the world. In 1933, he thought of the "nuclear chain reaction." This idea was key to understanding how to release energy from atoms. He also helped patent the first nuclear reactor with another scientist, Enrico Fermi. Later, in 1939, he helped write a famous letter for Albert Einstein to sign. This letter led to the start of the Manhattan Project, which developed the atomic bomb.
Contents
Early Life and Education
Leó Szilárd grew up in Budapest, Hungary. Even as a young boy, he was very curious and loved to learn. He studied engineering at the Budapest University of Technology. Later, he moved to Germany to study physics. He earned his Ph.D. from the University of Berlin in 1926. During this time, he worked with many famous scientists.
Moving to a New Home
In the 1930s, the political situation in Germany became difficult. Szilárd, who was Jewish, left Germany in 1933 to escape danger. He moved to London, England, and later to the United States in 1938. He continued his important scientific work in his new home.
The Nuclear Chain Reaction
In 1933, while in London, Leó Szilárd had a groundbreaking idea. He was thinking about how atoms could release a lot of energy. He realized that if you could split one atom, it might release particles that could split other atoms. This would create a "chain reaction."
How It Works
Imagine a line of dominoes falling. When one domino falls, it knocks over the next, and so on. A nuclear chain reaction is similar. When a neutron (a tiny particle) hits an atom, it can split the atom. This splitting releases more neutrons, which then hit other atoms, causing them to split too. This process releases a huge amount of energy very quickly. Szilárd was the first to think of this idea and how it could be used.
Developing the Nuclear Reactor
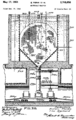
Szilárd's idea of a chain reaction was very important. It showed how to create a controlled release of nuclear energy. He worked with Italian physicist Enrico Fermi to turn this idea into reality.
The First Reactor
In 1942, Szilárd and Fermi built the world's first self-sustaining nuclear reactor. It was called Chicago Pile-1 (CP-1). This reactor showed that a nuclear chain reaction could be controlled. This was a huge step forward for science and technology. It opened the door for using nuclear energy for many purposes, like generating electricity.
The Einstein-Szilárd Letter
As World War II began, Szilárd worried that Germany might try to build powerful new weapons using nuclear energy. He knew that the United States needed to start its own research.
A Warning to the President
In 1939, Szilárd wrote a letter to President Franklin D. Roosevelt of the United States. He explained the possibility of a nuclear chain reaction and how it could lead to very powerful bombs. He asked his friend, the famous scientist Albert Einstein, to sign the letter. Einstein's signature made the letter even more impactful. This letter convinced President Roosevelt to start a secret research project.
The Manhattan Project
The letter signed by Einstein and written by Szilárd led to the creation of the Manhattan Project. This was a top-secret research and development project during World War II. Its goal was to build the first atomic bomb.
Role in the Project
Szilárd worked on the Manhattan Project. He helped develop the technology needed for the atomic bomb. However, after the war, he became very concerned about the use of nuclear weapons. He believed that these powerful weapons should be controlled internationally to prevent future wars. He spent the rest of his life working for peace and nuclear disarmament.
Later Life and Legacy
After the war, Leó Szilárd shifted his focus from nuclear physics to biology. He became a professor at the University of Chicago. He also worked at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies. He continued to invent and explore new scientific ideas.
A Visionary Scientist
Leó Szilárd was a true visionary. He not only had brilliant scientific ideas but also thought deeply about the impact of science on society. He is remembered for his key role in the development of nuclear energy and for his efforts to promote peace.
Images for kids
-
Szilard and Norman Hilberry at the site of CP-1, at the University of Chicago, some years after the war. It was demolished in 1957.
See also
 In Spanish: Leó Szilárd para niños
In Spanish: Leó Szilárd para niños