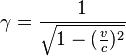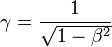Lorentz factor facts for kids
The Lorentz factor is a special number that helps us understand how things change when they move super, super fast – almost as fast as light! It tells us how much time, length, and even an object's "heaviness" (its mass) can stretch or shrink. This idea comes from the work of a Dutch scientist named Hendrik Lorentz.
Imagine you're on a super-fast spaceship. The Lorentz factor helps explain why time might slow down for you, or why things outside your window might look shorter.
Here's the math formula for the Lorentz factor, which is shown by the Greek letter gamma (γ):
In this formula:
- v is the speed of the object (like your spaceship).
- c is the speed of light.
The part `(v/c)` is often called beta (β). So, the formula can also look like this:
How Fast is Fast?
Have you ever heard of classical relativity? It's a simple idea. Imagine you throw a ball at 50 miles per hour (mph) while you are running at 5 mph. Someone watching you would see the ball traveling at 55 mph.
But for you, the ball still moves away from you at 50 mph. Both you and your friend are right! You just see things differently because you are moving with the ball.
Now, let's talk about the speed of light. It's incredibly fast: about 670,616,629 mph! What if you were in a car going half the speed of light (0.5c) and turned on your headlights? Would the light move away from you at 1.5c?
No, it turns out the speed of light (c) is always the same, no matter how fast you are moving. This is a key part of how the universe works!
Time Travel (Sort Of)!
When a clock moves very fast, it actually ticks a tiny bit slower. This slowing down is by the Lorentz factor (γ).
A famous idea called the twin paradox helps explain this. Imagine two twins. Twin A stays on Earth. Twin B travels very fast, close to the speed of light, for a few years.
When Twin B comes back to Earth, they would be much younger than Twin A! This is because Twin B experienced less time. For example, if Twin B left at age 20 and traveled at 90% the speed of light (.9c) for 10 years (from their point of view), they would be 30 when they returned. But Twin A on Earth would be almost 43!
Twin B wouldn't notice time slowing down at all. To them, everything would seem normal. But if they looked out their spaceship window, it would seem like the universe outside was moving slower. So, time really is different for different observers!
Shrinking Things
Things also get shorter in the direction they are moving when they travel at super-fast speeds. This is called length contraction.
During Twin B's journey, they would notice something strange about the universe outside their window. It would look shorter, or "contracted," in the direction their spaceship was flying. The amount things shrink is also related to the Lorentz factor (γ).
Getting Heavier
When objects move at very high speeds, their "relativistic mass" also increases. This means they become harder to push and speed up even more.
Imagine trying to push a car. It's hard! Now imagine that car getting heavier and heavier the faster it goes. That's what happens to objects moving close to the speed of light. By the time you reach 99.9999% the speed of light, you would need a huge amount of force to go even a tiny bit faster. This is why nothing with mass can ever reach the actual speed of light.
Still, if you travel a bit slower, like 90% of the speed of light, your mass only grows by about 2.3 times. So, while reaching the speed of light is impossible, getting very close to it might be possible – if you have enough power!
See also
 In Spanish: Factor de Lorentz para niños
In Spanish: Factor de Lorentz para niños