Mangarla language facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Mangarla |
|
|---|---|
| Mangala | |
| Native to | Australia |
| Region | Western Australia |
| Ethnicity | Mangala people |
| Native speakers | 68 (2016 census) |
| Language family |
Pama–Nyungan
|
| Dialects |
Juwarliny
|
| AIATSIS | A65 |
|
|
Mangarla, also spelled Mangala, is an Aboriginal language from Western Australia. It belongs to the Pama–Nyungan language family, which is a large group of Aboriginal languages. The Mangarla language is spoken by the Mangala people who live in the north-western part of the Great Sandy Desert, which is inland from the coast.
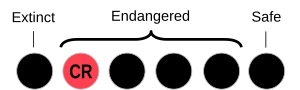
Sadly, Mangarla is a critically endangered language. This means that very few people still speak it, and it is at high risk of disappearing completely. According to the 2016 census, only about 68 people speak Mangarla. Efforts are being made to help keep the language alive for future generations.
Sounds of Mangarla
The Mangarla language has a sound system that is very similar to many other Aboriginal languages in Australia. It uses a specific set of sounds to form words.
Consonant Sounds
Mangarla has 17 different consonant sounds. These are sounds like 'p', 'k', 'm', and 'n'. Some of these sounds are made using different parts of the mouth, such as the lips, the back of the throat, or the tongue.
Vowel Sounds
Unlike English, which has many vowel sounds, Mangarla has only three main vowel sounds. These are similar to the 'ee' sound in "see", the 'oo' sound in "moon", and the 'ah' sound in "father". These three simple vowel sounds are common in many Australian Aboriginal languages.
 | Kyle Baker |
 | Joseph Yoakum |
 | Laura Wheeler Waring |
 | Henry Ossawa Tanner |

