Modulation facts for kids
Modulation is a cool way we change a wave to carry information, like sounds or data. Imagine you want to send a secret message across a room using a flashlight. You could blink the light on and off in a special code. That's a bit like modulation!
In radio, TV, and internet, we use invisible waves to send signals. These waves are called "carrier waves." Modulation is when we change some part of this carrier wave to add our message to it. It's like putting your message inside a special delivery box (the carrier wave) so it can travel far.
Contents
What is Modulation?
Modulation is the process of changing a carrier wave to put information on it. A carrier wave is a steady, repeating wave that travels through the air or cables. It doesn't carry any information by itself, just like an empty truck. When we modulate it, we make the truck carry a load, which is our message.
How Radio Waves Carry Information
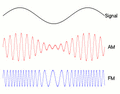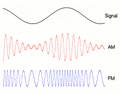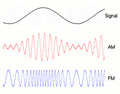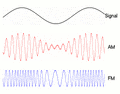
Radio stations use modulation to send music and voices to your radio. They take a high-frequency carrier wave and change it based on the sound they want to send. The two main ways they do this are Amplitude Modulation (AM) and Frequency Modulation (FM).
Amplitude Modulation (AM) Explained
With Amplitude Modulation (AM), we change the strength (or height) of the carrier wave. Think of it like making the flashlight beam brighter or dimmer to send your message. When you listen to an AM radio station, the sound you hear makes the radio wave stronger or weaker. The faster the wave changes its strength, the higher the pitch of the sound. AM radio waves can travel very far, especially at night, but they can also pick up a lot of static and noise.
Frequency Modulation (FM) Explained
With Frequency Modulation (FM), we change the frequency (how often the wave repeats) of the carrier wave. Imagine changing how quickly you blink your flashlight to send your message. When you listen to an FM radio station, the sound makes the radio wave speed up or slow down its wiggles. FM signals usually sound much clearer than AM signals because they are less affected by electrical noise. However, FM signals don't travel as far as AM signals.
Sending Digital Messages
Modulation isn't just for sounds! It's also super important for sending digital information, like the data from your computer or phone. Digital information is made of ones and zeros (binary code).
How Digital Signals Change Waves
For digital signals, we use different types of modulation. For example, in Phase-shift keying, the wave's starting point (its "phase") is shifted to represent a one or a zero. In Frequency-shift keying, the wave's frequency is changed between two or more values to represent different bits of data. These methods help computers talk to each other over long distances, making the internet and mobile phones work!
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Modulación (telecomunicación) para niños
In Spanish: Modulación (telecomunicación) para niños