One-line diagram facts for kids
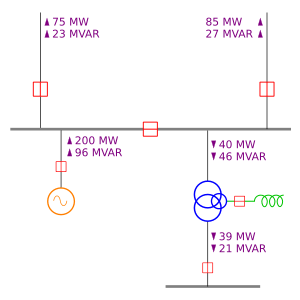
The one-line diagram (also called a single-line diagram) is a special drawing that shows how a three-phase electrical system works in a simple way. It's used a lot in places that deal with electricity, like power plants or big factories. Each part of the electrical system, like a generator or a transformer, has its own unique symbol in the diagram. Even though it shows a three-phase system (which usually has three wires), the diagram only draws one wire to represent all three. This makes it much easier to understand and plan electrical systems.
Contents
What is a One-Line Diagram?
A one-line diagram is like a simplified map of an electrical system. Imagine you have a very complex road map with many lanes for each road. A one-line diagram is like showing just one line for each road, even if it has many lanes. This helps engineers and technicians see the main connections and how electricity flows.
Why are One-Line Diagrams Used?
One-line diagrams are super helpful for several reasons:
- Planning: They help engineers design new electrical systems or make changes to old ones. It's easier to see the big picture.
- Troubleshooting: If there's a problem, like a power outage, these diagrams help quickly find where the issue might be.
- Safety: They show where safety devices, like circuit breakers, are located. This is important for keeping people safe.
- Communication: Everyone working on an electrical project can understand the system using these standard diagrams.
How are Electrical Parts Shown?
Each part of an electrical system has a special symbol. For example:
- A generator (which makes electricity) has a specific symbol.
- A transformer (which changes voltage) has another symbol.
- Circuit breakers (which protect the system) also have their own symbols.
These symbols are standard, so anyone who knows about electrical diagrams can understand them, no matter where they are from.
What Does "Three-Phase" Mean?
When we talk about "three-phase" electricity, it's a very common way to send a lot of power over long distances. It's like having three waves of electricity working together. Big buildings, factories, and power grids use three-phase power because it's very efficient. A one-line diagram simplifies this by showing just one line, even though it represents all three phases working together.
Key Features of One-Line Diagrams
One-line diagrams focus on showing the main connections and important information. They don't show every tiny wire or detail.
- They show how power flows from where it's made (like a power plant) to where it's used (like a factory or a home).
- They include important numbers, like the voltage levels at different points in the system.
- They also show where protective devices are placed to prevent damage from things like short circuits.
Where are They Used?
You can find one-line diagrams in many places:
- Power Plants: To show how electricity is generated and sent out.
- Electrical Substations: These are places where electricity voltage is changed for distribution.
- Large Buildings: To plan and manage the electrical system for offices, hospitals, or schools.
- Industrial Facilities: Factories use them to understand the power supply for their machines.
One-line diagrams are a simple but powerful tool that helps people work with electricity safely and efficiently.
See also
 In Spanish: Esquema unifilar para niños
In Spanish: Esquema unifilar para niños