Open Shortest Path First facts for kids
Open Shortest Path First (often called OSPF) is a special set of rules, or a "protocol," that helps computers find the best way to send information across a network or the internet. Think of it like a GPS for data packets! It figures out the quickest route for your messages to travel from one computer to another.
OSPF is based on a clever idea called Dijkstra's algorithm, which is a famous way to find the shortest path between points. The IETF, a group that sets standards for the internet, has made OSPF an official standard. It's mainly used inside a single organization's network to guide packets of data efficiently.
How OSPF Works: Finding the Best Path
OSPF helps routers, which are like traffic cops for network data, decide the best path for information. It does this by looking at how "expensive" or "fast" different paths are. The goal is always to find the "shortest" or "cheapest" path.
Why Networks Need OSPF
Imagine a huge city with many roads. Without a good map or GPS, cars might get lost or take very long routes. Computer networks are similar! They need a system to guide data packets efficiently. OSPF provides this system, making sure data gets where it needs to go quickly and reliably. It's especially useful in large, complex networks.
OSPF's Role in Routing Data
OSPF is an interior gateway protocol. This means it works within a single "domain" or "area" of a network, like inside a school's network or a company's network. It's not usually used to send data between completely different organizations, but rather within one big network.
Building a Network Map
OSPF routers constantly talk to each other. They share information about their connections and the "cost" of sending data over those connections. This information helps each router build a complete map of the network. Once a router has this map, it can use Dijkstra's algorithm to calculate the shortest path to any other part of the network.
Keeping the Map Updated
Networks can change. New connections might be added, or old ones might break. OSPF is designed to react quickly to these changes. If a link goes down, routers will update their maps and find a new best path, often in just a few seconds. This makes networks very reliable.
Key Concepts in OSPF
OSPF uses a few important ideas to manage large networks.
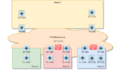
OSPF Areas: Dividing the Network
To make managing big networks easier, OSPF can divide a network into smaller sections called "areas." Think of these as different neighborhoods in a city.
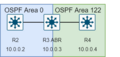
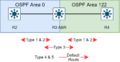
The Backbone Area
Every OSPF network has a special area called the backbone area, also known as Area 0. This is like the main highway system that connects all the other neighborhoods (areas). All other areas must connect to the backbone area. This design helps keep the network organized and efficient.
Connecting Areas with Routers
Routers that connect different areas are called Area Border Routers (ABRs). They know about the routes within their own area and also how to reach other areas through the backbone.
Types of OSPF Networks
OSPF can work in different ways depending on the type of network connection.
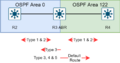
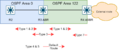
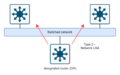
Broadcast Networks
In networks where one message can be sent to many devices at once (like an Ethernet network), OSPF uses a special router called a Designated Router (DR) and a Backup Designated Router (BDR). These routers help manage the flow of OSPF information and prevent too much chatter between all the routers.
Point-to-Point Networks
For simple connections between just two routers, OSPF works directly without needing a DR or BDR. This is common for connections over long distances.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Open Shortest Path First para niños
In Spanish: Open Shortest Path First para niños
 | Bessie Coleman |
 | Spann Watson |
 | Jill E. Brown |
 | Sherman W. White |