Operation Charioteer facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Charioteer |
|
|---|---|
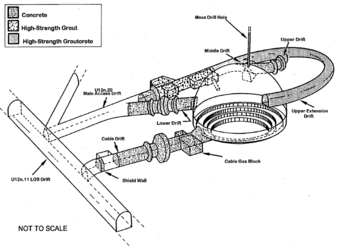
Mill Yard test underground cavity schematic
|
|
| Information | |
| Country | United States |
| Test site | NTS Area 12, Rainier Mesa; NTS Area 19, 20, Pahute Mesa; NTS, Areas 1–4, 6–10, Yucca Flat |
| Period | 1985–1986 |
| Number of tests | 16 |
| Test type | underground cavity in tunnel, underground shaft, tunnel |
| Max. yield | 140 kilotonnes of TNT (590 TJ) |
| Navigation | |
| Previous test series | Operation Grenadier |
| Next test series | Operation Musketeer |
Operation Charioteer was a group of 16 nuclear tests carried out by the United States. These tests happened between 1985 and 1986. They took place deep underground at the Nevada Test Site. This series of tests came after Operation Grenadier and before Operation Musketeer.
Contents
What Was Operation Charioteer?
Operation Charioteer was a series of experiments. The main goal was to test and improve nuclear weapons. Scientists also used these tests to learn more about how nuclear explosions affect different materials and equipment. All 16 tests were done underground to help contain the explosions.
Where Did These Tests Happen?
All the tests in Operation Charioteer happened at the Nevada Test Site (NTS). This site is a large area in Nevada, USA, used for nuclear testing. The tests were spread across different parts of the NTS, including Rainier Mesa, Pahute Mesa, and Yucca Flat.
How Were the Tests Done?
The tests were conducted in a few different ways, but always underground:
- Underground Shafts: Most tests involved lowering the nuclear device down a deep, narrow hole called a shaft.
- Tunnels: Some tests took place inside long tunnels dug into mountainsides.
- Underground Cavities: One test, called Mill Yard, used a special underground space or cavity.
Understanding Nuclear Yield
The "yield" of a nuclear test tells us how powerful the explosion was. It's measured in kilotons (kt) or tons (t) of TNT. For example, 1 kiloton (kt) is equal to the explosive power of 1,000 tons of TNT. The most powerful test in Operation Charioteer was Labquark, with a yield of 140 kilotons. This means it had the same explosive power as 140,000 tons of TNT!
Notable Tests in Operation Charioteer
During Operation Charioteer, scientists conducted several important tests:
- Goldstone (December 28, 1985): This test was part of Project Excalibur. This project aimed to develop special X-ray lasers powered by nuclear explosions.
- Mighty Oak (April 10, 1986): This test focused on how radiation from a nuclear blast affects military equipment. It helped engineers design stronger gear.
- Jefferson (April 22, 1986): This test checked an older nuclear weapon, the W56. It was a "stockpile confidence test" to make sure the weapon still worked as expected.
- Galveston (September 4, 1986): Similar to Jefferson, this test checked the B61 nuclear bomb to ensure it was still reliable.
- Labquark (September 30, 1986): This was the most powerful test in the series, with a yield of 140 kilotons. It was also part of the Project Excalibur X-ray laser research.
What is Venting?
Sometimes, during underground nuclear tests, small amounts of radioactive gases could escape to the surface. This is called "venting." Scientists carefully monitored for venting to ensure safety. Several tests in Operation Charioteer, like Mill Yard and Diamond Beech, had some venting detected.
 | Janet Taylor Pickett |
 | Synthia Saint James |
 | Howardena Pindell |
 | Faith Ringgold |

