Opuntia sulphurea facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Opuntia sulphurea |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Opuntia sulphurea, Province of Juyjuy, Argentina, 2325 meters above sea level | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Caryophyllales |
| Family: | Cactaceae |
| Genus: | Opuntia |
| Species: |
O. sulphurea
|
| Binomial name | |
| Opuntia sulphurea G.Don ex Salm-Dyck
|
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
Opuntia sulphurea is a type of cactus. It belongs to the Opuntia family, also known as prickly pears. These cacti are often round, green, and have long, thick spines. You can find Opuntia sulphurea in many places, especially around Argentina. It grows in dry areas, from flat lands to high up in the Andes mountains.
Because it can live in so many different places, there are a few types of Opuntia sulphurea. You can tell them apart by things like how many spines they have. All types have a bright yellow flower. This flower's color looks like sulfur, which is where the name sulphurea comes from.
Like other prickly pears, these cacti often grow in groups. They form big clumps that can be one to two meters wide. But unlike some other Opuntia species, Opuntia sulphurea stays low to the ground. This cactus is very tough. It can even survive in areas where cattle graze a lot.
In Spanish, people sometimes call this cactus "penca," "penquilla," or "penca chica." "Penca" means the main rib of a plant.
Contents
Where Does Opuntia sulphurea Grow?
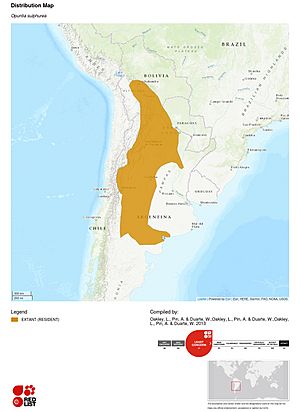
Opuntia sulphurea is mostly found in northwestern Argentina. This area stretches from the Mendoza province up to Juy Juy in the North. It also reaches the Buenos Aires province to the West. You can also see this cactus in parts of Paraguay, Bolivia, Chile, and western Brazil. There's even a group of them that started growing naturally in southern Queensland, Australia.
This cactus can live in many different places. It grows from areas at sea level up to heights of 3,500 meters (about 11,500 feet). Scientists have noticed that the fruit of Opuntia sulphurea can be different colors depending on where it grows.
There are three main types of fruit color:
- The sulphurea type has a yellow fruit. You can find this type from Mendoza to Catamarca province.
- The hildemannii type grows near the southern border of Bolivia and has red fruit.
- The pampeana type is named after the Pampas, a central area of Argentina.
These different types are not officially called subspecies, but they show how varied this cactus can be.
Habitat and Life Cycle of Opuntia sulphurea
This prickly pear cactus can grow well in many different environments. It especially likes dry, cool places. You often find it growing in rocky soil on hillsides, both at sea level and higher up. It can also grow in clay-filled soils.
Opuntia sulphurea likes soil that has a lot of nitrogen. Because of this, it often grows very well in areas where too many animals have grazed. In one study in Mendoza, Argentina, scientists found more Opuntia sulphurea plants in overgrazed areas. This cactus can even help show that overgrazing has happened.
The cactus spreads by dropping its stem parts, called cladodes. These cladodes can then grow into new plants. Cattle grazing in an area can actually help spread the cactus. This is because the cattle move the cladodes around.
Opuntia sulphurea is not in danger of disappearing. It can survive in many places and even thrive where other plants struggle. In fact, it can sometimes grow so much that it becomes an invasive species. This means it can take over areas and push out other plants.
What Does Opuntia sulphurea Look Like?
Opuntia sulphurea is special because it stays low to the ground. It grows wider instead of taller. It forms large clumps that are usually no higher than 40 centimeters (about 16 inches) off the ground.
The cactus is made of many oval-shaped pads. Each pad is about 15 to 20 cm long and 10 to 13 cm wide. These pads grow close together. The cactus has small bumps on its joints, which make its surface look wavy.
Most parts of the cactus have spines. Young spines can be pink, but as they get older, they turn gray or dark. These spines are thick, stiff, and sharp like needles. They can grow anywhere from 3 to 10 cm long and often twist as they get older.
The Opuntia sulphurea also grows a bright yellow flower. The flower is usually about 4 cm long. Its fruits can be yellowish or reddish.
Uses of Opuntia sulphurea
Right now, this cactus is not widely used. However, it could be a food source in the future. It can store a lot of water and has high amounts of protein and healthy fats. These fats come from a special acid found in its pads.
Some local communities already use this cactus for food. If more people started using it, Opuntia sulphurea could become very important for the economy. This is because it is tough and grows in many places.
See also
 In Spanish: Opuntia sulphurea para niños
In Spanish: Opuntia sulphurea para niños
 | Jackie Robinson |
 | Jack Johnson |
 | Althea Gibson |
 | Arthur Ashe |
 | Muhammad Ali |