Reverse osmosis facts for kids
Reverse osmosis is a clever way to clean water using a special filter called a membrane. Think of this membrane as a super-fine screen that lets water molecules pass through but blocks tiny particles, salt, and other unwanted stuff. The main reason we use it is to turn salty ocean water into fresh drinking water, a process called desalination. But it can also clean water for many other uses, like in homes or industries.
Contents
What is Reverse Osmosis?
Reverse osmosis is a process that forces water through a very fine filter. This filter, or membrane, has tiny holes. These holes are so small that only water molecules can get through. Larger molecules, like salt or dirt, are left behind.
How is it Different from Regular Osmosis?
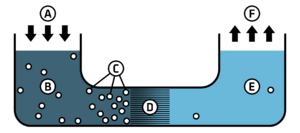
To understand reverse osmosis, let's first look at regular osmosis. Osmosis is a natural process where water moves from an area with less salt to an area with more salt, through a membrane. It tries to balance the saltiness on both sides.
Reverse osmosis does the opposite. We apply pressure to the salty water. This pressure forces the water to move from the salty side to the clean water side, against the natural flow of osmosis. It's like pushing water uphill!
Why Do We Use Reverse Osmosis?
Reverse osmosis is super important for several reasons:
- Making Drinking Water: It's a key method to get fresh water from the ocean or from water that's too salty to drink. Many dry regions rely on this technology.
- Cleaning Water for Homes: Some home water filters use reverse osmosis to make tap water taste better and remove impurities.
- Industrial Uses: Factories use it to get very pure water for making medicines, electronics, or for power plants.
- Recycling Water: It can help clean wastewater so it can be used again, which saves precious water resources.
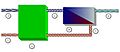
How Does a Reverse Osmosis System Work?
A typical reverse osmosis system has a few main parts:
- Pre-filters: Before the water reaches the main membrane, it often goes through filters that remove larger particles like sand or rust. This protects the delicate reverse osmosis membrane.
- The Membrane: This is the heart of the system. It's a very thin, layered material with microscopic pores. Water is pushed against this membrane.
- Pressure Pump: A pump creates the high pressure needed to force water through the membrane. This pressure is what makes "reverse" osmosis happen.
- Post-filters: After passing through the membrane, the clean water might go through another filter to improve its taste or quality even more.
- Drain: The concentrated salty water that doesn't pass through the membrane is sent down a drain. This water contains all the impurities that were removed.
The Membrane: A Closer Look
The reverse osmosis membrane is made of special materials, often thin plastic films. These films are usually rolled up tightly to fit into a small space, creating a large surface area for water to pass through. The tiny holes in the membrane are smaller than most bacteria, viruses, and even many dissolved salts.
History of Reverse Osmosis
The idea of osmosis was first observed in 1748 by Jean-Antoine Nollet. However, it wasn't until the mid-20th century that scientists figured out how to reverse this process effectively.
In the 1950s, researchers at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), including Sidney Loeb and Srinivasa Sourirajan, made a big breakthrough. They developed membranes that could handle high pressure and effectively remove salt from seawater. This discovery made reverse osmosis a practical way to get fresh water. Since then, the technology has improved a lot, making it more affordable and efficient.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Ósmosis inversa para niños
In Spanish: Ósmosis inversa para niños