Richard Hill Norris facts for kids
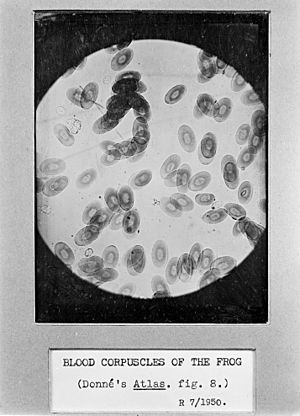
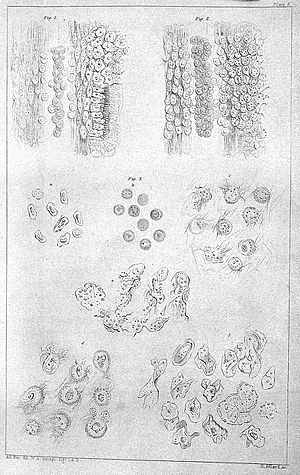
Richard Hill Norris (1830-1916) was a British scientist who studied how living things work (a physiologist). He was also a photographer and was interested in spiritualism. In the 1880s, he started taking tiny pictures of blood cells using a microscope. This made him a leader in a field called microphotography. In 1856, he created a special type of photographic plate called the dry collodion plate.
About His Life
Norris studied medicine at the University of Edinburgh. He became very interested in microphotography early on, especially in taking pictures of frog blood.
In 1856, he invented the first dry collodion photographic plate. This was a big step forward because it made photography easier. Two years later, in 1858, he started the Patent Dry Collodion Plate Company in Birmingham. This was one of the first companies in the world to make photographic materials for sale.
From 1862 to 1891, he taught about how the body works (physiology) at Queens College in Birmingham.
In 1878, he became a Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. This is a special honor given to important scientists.
Norris continued to invent new ways to take photos. In 1888, he was still getting patents for his photographic ideas. By 1890, he teamed up with Harold William Southall to start the Birmingham Dry Collodion Plate and Film Company. They built a large factory in Yardley, Birmingham, which started making products in 1893. However, this company did not succeed and closed in 1895.
Norris also worked with another scientist, George Gore, to study how metals change when they are heated and cooled. They did this research at the Institute of Scientific Research in Birmingham.
His Interest in Spiritualism
Richard Hill Norris was also very interested in spiritualism. This is a belief that the spirits of dead people can communicate with the living. He thought of himself as an amateur medium, someone who could talk to spirits. He took part in seances (meetings where people try to contact spirits) and tried automatic writing, where a person writes without consciously controlling what they write.
He believed in ideas like mesmerism and hypnotism, which involve using a person's mind to influence their body or thoughts. He studied cases like that of Christine Beauchamp, a famous example of someone with multiple personalities. Even though he had strong beliefs about spiritualism, he did not publish his ideas. However, he wrote letters to other people who were interested in spiritualism, like Alfred Russel Wallace and William Crookes.
His Family
In 1852, Richard Hill Norris married Ann (1827-1901). They had a son named Richard Hill Norris (1853-1919), who also became a doctor. His other sons were Arthur Kingsley Norris and Benjamin Stuart Norris. His brother, Joseph Norris, was also a photographer.