Sebaceous hyperplasia facts for kids
Sebaceous hyperplasia is a common skin condition. It causes small, harmless bumps to form on the skin. These bumps are made when tiny oil glands in your skin, called sebaceous glands, become larger than normal. They are usually filled with a natural oil called sebum.
Contents
What is Sebaceous Hyperplasia?
Sebaceous hyperplasia happens when your sebaceous glands grow too much. These glands are found all over your skin, except on the palms of your hands and the soles of your feet. Their job is to make sebum, which helps keep your skin and hair moisturized. When these glands get bigger, they can create small, soft bumps on your skin.
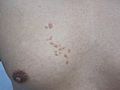
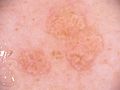
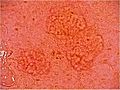
What Do the Bumps Look Like?
The bumps from sebaceous hyperplasia are usually:
- Small, often 2 to 9 millimeters across.
- Yellowish or flesh-colored.
- Soft to the touch.
- Often have a small dip or dent in the center.
- They can appear alone or in groups.
They are most often found on the face, especially on the forehead and cheeks. But they can also show up on the chest, back, or other parts of the body.
Is It Harmful?
No, sebaceous hyperplasia is not harmful. The bumps are non-malignant, which means they are not cancerous. They do not turn into cancer. However, sometimes people might not like how they look, or they might get irritated if they are in a place where clothing rubs against them. Squeezing them can sometimes make sebum come out, but this is not recommended as it can cause irritation or even a small infection.
Who Gets Sebaceous Hyperplasia?
This skin condition is most common in adults, especially those who are middle-aged or older. It can affect both men and women. It's not something you catch from someone else; it's not contagious.
What Causes It?
The exact cause of sebaceous hyperplasia isn't fully known, but several things can play a role:
- Aging: As people get older, their sebaceous glands can sometimes become larger.
- Hormones: Hormones, especially androgens (like testosterone), are thought to be involved. These hormones can affect how sebaceous glands grow.
- Sun Exposure: Spending a lot of time in the sun might also increase the chance of developing these bumps.
- Genetics: Sometimes, it might run in families, meaning if your parents have it, you might be more likely to get it too.
- Medications: Certain medicines, like those used after an organ transplant, can sometimes lead to sebaceous hyperplasia.
How is Sebaceous Hyperplasia Diagnosed?
Usually, a doctor, like a dermatologist (a skin doctor), can tell if you have sebaceous hyperplasia just by looking at your skin. The bumps have a very distinct look.
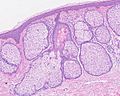
When Might a Biopsy Be Needed?
Sometimes, if a bump looks unusual or the doctor isn't sure, they might do a small procedure called a biopsy. This involves taking a tiny piece of the skin bump to look at it under a microscope. This helps them confirm it's sebaceous hyperplasia and not something else.
How is Sebaceous Hyperplasia Treated?
Since sebaceous hyperplasia is harmless, treatment is usually not needed unless someone wants the bumps removed for cosmetic reasons (because they don't like how they look).
Common Treatment Options
There are several ways doctors can remove these bumps:
- Cryotherapy: This uses very cold liquid nitrogen to freeze and destroy the bumps.
- Electrocautery: This uses heat from an electric current to burn off the bumps.
- Laser Therapy: Different types of lasers can be used to remove or reduce the size of the bumps.
- Topical Treatments: Sometimes, creams or gels containing certain ingredients, like retinoids, might be used to help reduce the size of the bumps over time.
- Photodynamic Therapy: This involves applying a special solution to the skin and then using a light to activate it, which helps destroy the sebaceous glands.
It's important to remember that even after treatment, new bumps can sometimes form in other areas, or the treated ones might come back.
Living with Sebaceous Hyperplasia
Most people with sebaceous hyperplasia don't need to do anything special. If you have these bumps, it's a good idea to:
- Protect your skin from the sun: Using sunscreen and wearing protective clothing can help.
- Avoid squeezing the bumps: This can cause irritation or lead to a small infection.
- Talk to a doctor: If you are worried about the bumps or want them removed, a dermatologist can give you the best advice.
Remember, sebaceous hyperplasia is a common and harmless skin condition.
Images for kids