Myopia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Myopia |
|
|---|---|
| Synonyms | near-sightedness, short-sightedness |
 |
|
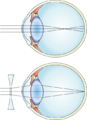
| Diagram showing changes in the eye with myopia | |
| Symptoms | Distant objects look blurry, headaches, tired eyes |
| Complications | Rare serious eye problems (like Retinal detachment) |
| Usual onset | Often starts in childhood |
| Duration | Usually lasts a lifetime |
| Causes | Eye grows too long; linked to genes and environment |
| Risk factors | Reading/screen time up close, not enough time outside, family history |
| Diagnostic method | Complete Eye examination |
| Prevention | Spending time outdoors helps |
| Treatment | Eyeglasses, contact lenses, or surgery |
| Medication | Special eye drops (like low-dose atropine) |
| Prognosis | Usually stable after teenage years |
| Frequency | Affects about 30% of people worldwide |
| Deaths | Not deadly |
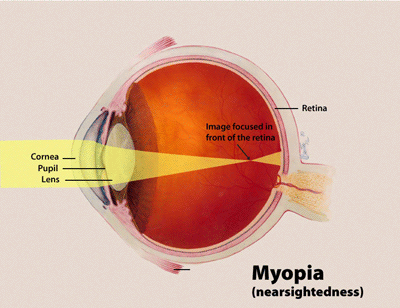
Myopia, often called near-sightedness or short-sightedness, is a very common eye condition. If you have myopia, you can see things clearly when they are close to you, but objects far away look blurry or fuzzy. This happens because the light entering your eye focuses slightly in front of the retina (the light-sensing layer at the back of the eye), instead of directly on it.
Myopia usually develops because the eyeball grows a little too long from front to back. It is a type of refractive error, meaning the eye doesn't bend light correctly. If myopia is severe (called high myopia), it can increase the risk of other eye problems later in life, like cataracts or glaucoma.
The good news is that myopia is easily corrected using eyeglasses or contact lenses. Spending more time outside during childhood may help reduce the risk of developing it. Myopia affects about 30% of people globally, making it one of the most common vision issues worldwide.
Contents
Understanding Near-Sightedness (Myopia)
What Causes Blurry Distance Vision?
When you have myopia, your eye focuses light incorrectly. Imagine your eye is like a camera. For clear vision, the image must focus perfectly on the film (the retina). In a myopic eye, the focus point lands too soon—in front of the retina.
This usually happens because the eyeball has grown slightly longer than normal. Less commonly, the lens or cornea (the front surface of the eye) might be too curved, making the focusing power too strong.
Signs You Might Have Myopia
The main sign of myopia is that distant objects look blurry. You might struggle to read the whiteboard at school, see street signs clearly, or watch a movie screen.
Other common symptoms include:
- Squinting often to try and see far away objects.
- Feeling eye strain or tired eyes after focusing.
- Getting headaches, especially after school or long periods of looking far away.
Myopia often starts when children are around 8 to 15 years old and can gradually worsen during the teenage years.
Why Does Myopia Develop?
Scientists believe myopia is caused by a mix of two main factors: your genes and your environment (how you use your eyes).
Genetic Factors and Family History
A risk for myopia can be inherited from your parents. If one or both of your parents have myopia, you are more likely to develop it too. Studies show that genes play a significant role in determining the shape and size of your eyeball.
Environmental Factors and Lifestyle
The way you spend your time, especially during childhood, strongly influences whether myopia develops.
Spending Time Outdoors
Research shows that children who spend more time outside have a lower risk of developing myopia. This protective effect is thought to be linked to exposure to bright sunlight. Sunlight helps the eye release a chemical called dopamine, which is believed to help control the growth of the eyeball.
In places like Taiwan, government programs encourage students to spend at least 80 minutes outdoors every day to help combat rising myopia rates.
Near Work and Screen Time
Activities that require intense focus on close objects—like reading, studying, or using digital screens (phones, tablets, computers)—are called "near work." Spending too much time on near work, especially without breaks, is a major risk factor for myopia.
A 2025 analysis of many studies found that every extra hour of daily screen time was associated with a 21% higher chance of having myopia. It is important to take regular breaks when doing near work.
Getting a Myopia Diagnosis
If you or your parents notice signs of blurry distance vision, you should visit an eye care professional (an optometrist or ophthalmologist).
The eye doctor performs a complete Eye examination. They use special tools to measure how light focuses in your eye. Sometimes, they use special eye drops (called cycloplegics) to temporarily relax the focusing muscles of the eye. This ensures they get an accurate measurement of your refractive error.
Classifying Myopia Severity
Myopia is measured in units called diopters (D). The more negative the number, the stronger the correction needed.
- Low Myopia: Usually between -0.50 and -3.00 D.
- Moderate Myopia: Usually between -3.00 and -6.00 D.
- High Myopia: Myopia of -6.00 D or more. High myopia requires careful monitoring because it is linked to a higher risk of serious eye conditions later in life.
Treating and Controlling Myopia
The goal of treatment is to correct the blurry vision so you can see clearly.
Corrective Lenses: Glasses and Contacts
The simplest and safest way to correct myopia is using eyeglasses. The lenses in glasses are shaped to bend light so it focuses perfectly on your retina. They have a negative power (like -2.00 D) because they are divergent lenses.
Contact lenses are small plastic lenses worn directly on the eye. They offer a wider field of vision than glasses. However, they require careful cleaning and handling to avoid the risk of eye infections.
Slowing Down Myopia Progression
For children and teenagers whose myopia is getting worse quickly, doctors may recommend methods to slow down this progression:
- Special Lenses: Some glasses or specially designed contact lenses are used to help control how fast the eye lengthens.
- Atropine Eye Drops: Low-dose atropine eye drops are sometimes prescribed. These drops help relax the eye's focusing mechanism and have been shown to slow the worsening of myopia in children.
Refractive Surgery Options
For adults whose vision has stabilized (usually after age 21), refractive surgery can permanently change the shape of the cornea to correct vision.
- LASIK and PRK: These procedures use a laser to reshape the cornea. They are popular ways to reduce or eliminate the need for glasses or contact lenses.
- Orthokeratology (Ortho-K): This involves wearing special rigid contact lenses overnight. These lenses temporarily reshape the cornea so you can see clearly during the day without glasses or contacts. Ortho-K can also help slow down myopia progression.
History and Global Impact
The difference between near-sighted and far-sighted people was noted thousands of years ago by Aristotle. The term "myopia" comes from ancient Greek words meaning "to close the eye," referring to the habit of squinting to see better.
The first glasses designed to correct myopia appeared around 1451. In 1604, Johannes Kepler explained scientifically that myopia happens because light focuses in front of the retina.
Myopia Around the World
Myopia is incredibly common. It affects about 1.5 billion people globally. Rates are especially high in many Asian countries, where up to 90% of young people may have myopia.
In the United States, the prevalence of myopia has increased significantly, rising from about 25% in the early 1970s to 42% in the early 2000s. This increase worldwide is strongly linked to changes in lifestyle, including less time spent outdoors and more time spent on close-up activities.
Uncorrected myopia is a leading cause of vision impairment globally. Ensuring everyone has access to eye exams and corrective lenses is a major worldwide public health goal.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Miopía para niños
In Spanish: Miopía para niños