Squamous cell carcinoma facts for kids
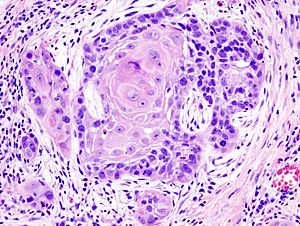
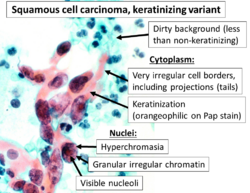
Squamous-cell carcinoma (SCC), also known as epidermoid carcinoma, is a type of cancer. It starts in flat cells called squamous cells. These cells are found on the surface of your skin, inside hollow organs, and in the lining of your breathing and digestive systems.
Even though they all share the name "squamous-cell carcinoma," these cancers can act differently depending on where they are in the body. They might show different signs, progress in different ways, and respond to treatment differently.
Contents
Where SCC Can Be Found
Squamous-cell carcinoma can appear in many parts of the body. A virus called human papillomavirus (HPV) has been linked to SCCs in areas like the throat, lungs, fingers, and private parts.
Head and Neck
About 90% of head and neck cancer cases are squamous-cell carcinomas. These cancers can affect the mouth, nose, throat, and nearby areas.
Skin
Cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma is the second most common type of skin cancer. More than a million cases are found in the United States each year.
Thyroid Gland
When SCC starts in the thyroid gland (a gland in your neck), it can be a very serious type of cancer.
Esophagus
Esophageal cancer can be a squamous-cell carcinoma. The esophagus is the tube that carries food from your mouth to your stomach. SCCs in the esophagus often happen closer to the mouth. Signs of this cancer include difficulty swallowing (especially solid foods) and painful swallowing. If the cancer is only in one spot, doctors might remove that part of the esophagus with surgery. If it has spread, treatments like chemotherapy and radiotherapy are often used.
Lungs
Squamous-cell carcinoma of the lung is often found in the center of the lungs. This type of lung cancer is mostly caused by smoking.
Prostate Gland
When SCC affects the prostate gland (a gland in males), it can be very aggressive. It is often hard to find early because it doesn't cause a common marker (PSA levels) to rise, so it's often diagnosed at a later stage.
Bladder
Most bladder cancers are a different type, but bladder cancer linked to a parasitic infection called schistosomiasis is often SCC.
How Doctors Find SCC
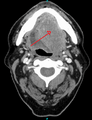
Doctors use different methods to find squamous-cell carcinoma. They will ask about your health history, do a physical examination, and might use medical imaging like X-rays or scans. To be sure, they usually need to do a biopsy. This means taking a small sample of the affected tissue to look at it closely under a microscope.
Understanding SCC
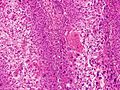
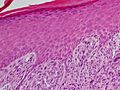
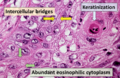
Cancer is a very broad term for many different diseases where cells grow out of control. Squamous-cell carcinomas are a large group within this family. All SCCs are thought to start when certain "stem cells" in the body's lining (epithelium) begin to divide too much and don't stop.
These cancers come from squamous cells, which are flat cells that line many areas of the body, including the skin. When these cancer cells first appear, they might be contained in one small area. This is called "carcinoma in situ" (meaning "in its original place"). At this stage, the tumor has not spread into nearby tissues.
If the cancer grows and breaks through its original boundaries, it is called "invasive" squamous-cell carcinoma. Once it becomes invasive, it can spread to other organs in the body. When cancer spreads to a new part of the body, it forms a "secondary tumor" or metastasis.
Prevention
What you eat can play a role in preventing skin cancers, including SCC. Some studies suggest that eating a lot of high-fat dairy foods might increase the risk of SCC tumors, especially for people who have had skin cancer before.
On the other hand, eating green leafy vegetables, raw vegetables, and fruits may help protect against SCC. Some research also suggests that eating whole milk, yogurt, and cheese might increase SCC risk in some people.
Eating a lot of meat and fatty foods can also increase the risk of SCC, especially for those who have had skin cancer in the past. Smoking tobacco and drinking a lot of beer and liquor are also linked to a higher risk of SCC.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Carcinoma espinocelular para niños
In Spanish: Carcinoma espinocelular para niños