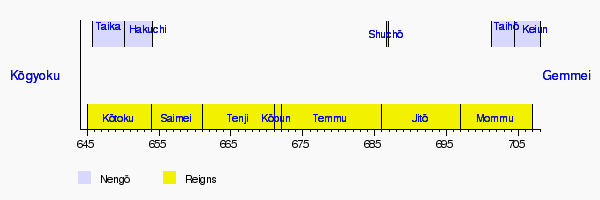
Taihō (大宝) was a special time period in Japanese history. It was a "Japanese era name," also called a nengō (年号). Think of it like a way to count years, similar to how we use BC or AD. This era came after a break in these special names, following the Shuchō period and before the Keiun period. The Taihō era lasted from March 701 to May 704. During this time, the ruler of Japan was Emperor Mommu (文武天皇).
History of the Taihō Era
The idea of using nengō (era names) in Japan was similar to a system used in China called nianhao. Using these era names was a big step for the Japanese Imperial court. It showed that their political power was growing stronger.
The Taihō era was named because gold was discovered on an island called Tsushima. This was an important event for Japan at the time.
Taihō Era Timeline
It's important to remember that the Japanese era names were not the same as the dates of an Emperor's reign.
Key Events of the Taihō Era
- 701 (Taihō 1): Plans were approved for a special group of people to travel to China. This group was called a "mission to the Tang court."
- 702 (Taihō 2): A very important set of laws was created. It was called the Taihō Code (大宝律令, Taihō-ritsuryō). These laws completely reorganized how the Japanese government worked. They finished the changes started by the earlier Taika Reforms.
- 701 (Taihō 2): A mission to the Tang court actually set sail. It was led by a person named Awata no Mahito (粟田真人). The diplomats traveled by ship. This trip was known as the "embassy of Taihō" because it began during this era.
Taihō Era Dates
| Taihō |
1st |
2nd |
3rd |
4th |
| Gregorian |
701 |
702 |
703 |
704 |
Related Pages
- National Diet Library, "The Japanese Calendar" -- historical overview plus illustrative images from library's collection
See also
 In Spanish: Taihō (era) para niños
In Spanish: Taihō (era) para niños
 In Spanish: Taihō (era) para niños
In Spanish: Taihō (era) para niños




