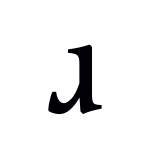Voiced alveolar and postalveolar approximants facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Alveolar approximant |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
| ɹ | |||
| ð̠˕ | |||
|
|||
| IPA number | 151 | ||
| Encoding | |||
| Entity (decimal) | ɹ |
||
| Unicode (hex) | U+0279 | ||
| X-SAMPA | r\ or D_r_o |
||
| Kirshenbaum | r |
||
|
|
|||
| ɹ̠ | |
|---|---|
|
|
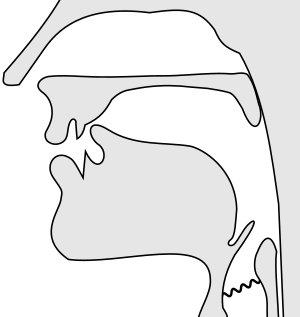
The voiced alveolar approximant is a special type of consonant sound. It's used in many spoken languages around the world. Think of it as a sound where your tongue gets close to the ridge behind your upper front teeth, but doesn't quite touch it to block the air completely.
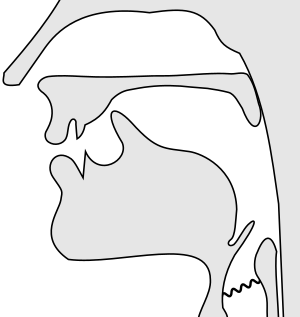
The International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) uses a special symbol for this sound: ⟨ɹ⟩. This symbol looks like a lowercase letter r that has been turned upside down. In English, the most common "r" sound is actually a bit different. It's called the voiced postalveolar approximant. This sound is made a little further back in your mouth. Its exact IPA symbol is ⟨ɹ̠⟩, but ⟨ɹ⟩ is often used because it's easier. Sometimes, you might even see the simple letter ⟨r⟩ used for English "r" sounds. However, in phonetics, ⟨r⟩ actually stands for a different sound called an alveolar trill, which is like a rolled "r."
There's also a sound called the "bunched r" or "molar r." It sounds very similar to the postalveolar approximant. You can make this sound by pulling your tongue back and bunching it up. The IPA symbols for this sound are ⟨ψ⟩ or ⟨ɹ̈⟩.
Contents
What Makes the Voiced Alveolar Approximant Special?
Sounds like the voiced alveolar approximant have several key features:
- Approximant: This means your tongue gets close to another part of your mouth, but doesn't fully block the airflow. The air just flows smoothly past.
- Alveolar: The sound is made by your tongue getting close to the alveolar ridge. This is the bumpy area right behind your upper front teeth.
- Voiced: When you make this sound, your vocal cords vibrate. You can feel this if you put your hand on your throat while saying it.
- Oral: The air comes out only through your mouth, not your nose.
- Central articulation: The air flows out over the center of your tongue.
- Pulmonic: The air that makes the sound comes from your lungs.
Where Can You Hear This Sound?
The voiced alveolar approximant, or sounds very similar to it, appear in many languages. Sometimes it's the main "r" sound, and sometimes it's a variation of another "r" sound.
Alveolar Approximant Sounds Around the World
Here are some examples of languages that use the alveolar approximant:
| Language | Example Word | How it Sounds (IPA) | Meaning | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albanian | gjelbr | [ˈɟʑɛlbəɹ] | 'green' | |
| Armenian | սուրճ | [suɹtʃ] | 'coffee' | (Classical Armenian) |
| Assamese | ৰঙা (rônga) | [ɹɔŋa] | 'red' | |
| Assyrian Neo-Aramaic | ܪܒ | [ɹɑbɑ] | 'many' | (Alqosh and Tyari dialects) |
| Bengali | আবার | [abaɹ] | 'again' | Especially in some Eastern dialects. |
| Burmese | ပရိဘောဂ | [pəɹḭbɔ́ɡa̰] | 'furniture' | Mostly in words borrowed from other languages. |
| Chukchi | ңирэк | [ŋiɹek] | 'two' | |
| Dahalo | káð̠˕i | [káð̠˕i] | 'work' | This sound is often a variation of another 'd' sound. |
| Danish | ved | [ve̝ð̠˕ˠ] | 'at' | A variation of the 'd' sound at the end of a word. |
| Dutch | door | [doːɹ] | 'through' | (Central and Western Netherlandic dialects) |
| Dutch | rat | [ɹat] | 'rat' | (Leiden dialect) |
| Faroese | róður | [ɹɔuwʊɹ] | 'rudder' | |
| German | Rebe | [ˈɹeːbə] | 'vine' | Found in some specific dialects like Siegerland and Silesian. |
| Greek | μέρα | [ˈmɛɹɐ] | 'day' | A variation of the 'r' sound in fast or casual speech. |
| Icelandic | bróðir | [ˈprou̯ð̠˕ir] | 'brother' | |
| Limburgish | maintenant | [ˈmæ̃ːn˦ð̠˕ənɑ̃ː˨] | 'now' | (Montfortian dialect) |
| Persian | فارسی | [fɒːɹˈsiː] | 'Persian' | A variation of the 'r' sound before certain consonants. |
| Portuguese | amor | [aˈmoɹˠ] | 'love' | In some Brazilian dialects, especially at the end of words. |
| Spanish | doscientos | [do̞ɹˈθje̞n̪t̪o̞s] | 'two hundred' | (Andalusian Spanish) |
| Spanish | invierno | [imˈbjeɹno] | 'winter' | In some dialects like Belizean, Caribbean Colombian, and Puerto Rican Spanish. |
| Swedish | starkast | [ˈs̪t̪äɹːkäs̪t̪] | 'strongest' | A variation of the 'r' sound. |
| Tagalog | parang | [paɹaŋ] | 'like-' | Used by younger speakers who are more familiar with English. |
| Turkish | artık | [aɹtɯk] | 'excess, surplus' | A variation of the 'r' sound at the end of a syllable. |
| Vietnamese | ra | [ɹa] | 'go out' | (Saigon dialect) |
| Zapotec | rdɨ | [ɹd̪ɨ] | 'pass' | (Tilquiapan Zapotec) |
Postalveolar Approximant Sounds
The postalveolar approximant is very common, especially for the "r" sound in English.
| Language | Example Word | How it Sounds (IPA) | Meaning | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | red | [ɹ̠ʷed] | 'red' | This is the typical "r" sound in most American, Australian, and British English. It's often made with rounded lips. |
| Igbo | rí | [ɹ̠í] | 'eat' | |
| Malay | راتوس / ratus | [ɹ̠ä.tos] | 'hundred' | Sometimes used instead of a rolled or flapped 'r'. |
| Maltese | malajr | [mɐˈlɐjɹ̠] | 'quickly' | In some dialects. |
| Shipibo | roro | [ˈd̠ɹ̠o̽ɾ̠o̽] | 'to break into pieces' | |
| Thai | กรุงเทพ / Krungthep | Bangkok | Can be a variation of the alveolar approximant. |
You can also find the [ɹ] sound as a variation of other "r" sounds in languages like Edo, Fula, Murrinh-patha, and Palauan.
Learn More About Sounds
- Index of phonetics articles
 | Janet Taylor Pickett |
 | Synthia Saint James |
 | Howardena Pindell |
 | Faith Ringgold |