Warji languages facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Warji |
|
|---|---|
| North Bauchi; B.2 West Chadic | |
| Geographic distribution: |
Darazo and Ningi LGAs, Bauchi State, Nigeria |
| Linguistic classification: | Afro-Asiatic
|
| Subdivisions: |
—
|
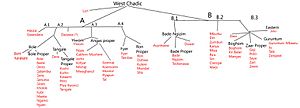 West Chadic per Newman (1977)
|
|
The Warji languages are a group of languages spoken mainly in Bauchi State, Nigeria. They are part of a larger language family called West Chadic languages. Think of it like a big tree: the Afro-Asiatic languages are the main trunk, Chadic languages are a big branch, West Chadic languages are a smaller branch, and the Warji languages are like a group of leaves on that branch.
These languages are important because they help us understand the history and culture of the people who speak them in Nigeria.
What Are Warji Languages?
The Warji languages are a special group of languages that are all related to each other. This means they share a common ancestor language from a long time ago. People in the Bauchi State of Nigeria use these languages every day to talk to each other, share stories, and keep their traditions alive.
There are several different languages within the Warji group. Each one is unique, but they also have many similarities because they come from the same language family.
Languages in the Warji Family
Here are some of the languages that belong to the Warji family:
- Pa'a
- Warji
- Diri
- Ciwogai
- Kariya (also known as Vinahə)
- Mburku
- Miya
- Siri
- Zumbun (also known as Jimbin)
- Ajawa (This language is no longer spoken, which is why it has a dagger symbol next to it. It means it's extinct.)
Each of these languages helps make the cultural tapestry of Nigeria rich and diverse.
Images for kids