Wavelet transform facts for kids
The wavelet transform is a special way to look at signals. Think of a signal as a sound wave or a picture. This transform helps us understand how a signal changes over time and at different frequencies. It's like taking a signal and breaking it down into many smaller, simpler waves called "wavelets."
We use wavelet transforms for many cool things. For example, they can help us remove unwanted noise from recordings. They can also help us find important features in data, like patterns in brain waves. Another big use is compressing data, which makes files smaller without losing too much quality. This is similar to how MP3s compress music.
Contents
What is a Wavelet?
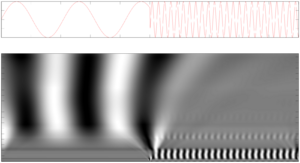
A wavelet is a small wave that starts and ends quickly. Unlike the waves we usually think of, which go on forever, wavelets are short bursts. Imagine a quick tap on a drum versus a long, continuous note from a flute. The drum tap is more like a wavelet.
Wavelets are special because they can change their shape. They can be stretched out to look at slow changes in a signal. They can also be squished together to look at fast, sudden changes. This flexibility makes them very useful for analyzing different parts of a signal.
How Wavelet Transforms Work
The wavelet transform works by comparing a signal to many different wavelets. It slides a wavelet along the signal, checking how well they match at each point. It also stretches and squishes the wavelet to see how it matches different parts of the signal.
When a wavelet matches a part of the signal well, it tells us something important about that part. For example, a stretched wavelet might pick up a slow, steady hum. A squished wavelet might pick up a sudden, sharp sound. By doing this, the transform creates a "map" of the signal. This map shows what frequencies are present at different times.
Continuous Wavelet Transform
The continuous wavelet transform looks at a signal in a very detailed way. It uses wavelets that can be stretched or moved by any tiny amount. This gives a very smooth and complete picture of the signal. It's like having an infinite number of magnifying glasses to look at every detail.
Discrete Wavelet Transform
The discrete wavelet transform is a more practical version. Instead of using every possible stretch and position, it uses specific, fixed steps. This makes it easier to use with computers. It's like taking snapshots at set intervals instead of a continuous video. This version is often used for things like image compression.
Dyadic Wavelet Transform
A common type of discrete wavelet transform is the dyadic wavelet transform. In this type, the wavelets are stretched by factors of two (like 2, 4, 8, 16, and so on). This makes it very efficient for computers to process. It's often used in digital signal processing.
Uses of Wavelet Transforms
Wavelet transforms are used in many different fields:
- Image and Audio Compression: They help make files smaller for things like JPEG 2000 images and some audio formats.
- Noise Reduction: They can separate useful information from unwanted noise in signals, like cleaning up a noisy recording.
- Medical Imaging: Used in things like MRI scans to process and analyze images of the body.
- Earthquake Prediction: Scientists use them to analyze seismic waves and look for patterns that might predict earthquakes.
- Financial Analysis: They can help find trends and patterns in stock market data.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Transformada ondícula para niños
In Spanish: Transformada ondícula para niños
 | Tommie Smith |
 | Simone Manuel |
 | Shani Davis |
 | Simone Biles |
 | Alice Coachman |