Yuman–Cochimí languages facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Yuman–Cochimí |
|
|---|---|
| Yuman | |
| Geographic distribution: |
Colorado River basin and Baja California |
| Linguistic classification: | Hokan ?
|
| Subdivisions: |
Cochimí †
Kiliwa
Delta–California
River
Pai
|
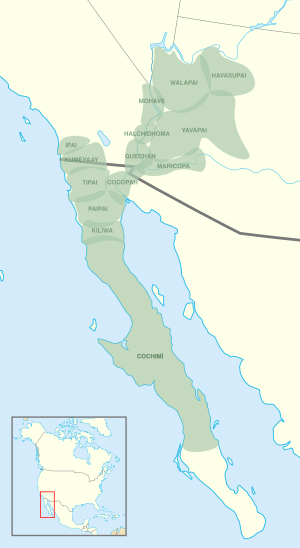 Pre-contact distribution of Yuman–Cochimí languages
|
|
The Yuman–Cochimí languages are a group of languages spoken by Native American people. These languages are found in areas like Baja California in Mexico, and parts of Arizona and California in the United States.
Sadly, the Cochimí language is no longer spoken today, as it died out in the late 1700s. Many other Yuman languages are also in danger of disappearing, meaning fewer and fewer people speak them.
What are Yuman–Cochimí Languages?
There are about a dozen (12) different Yuman languages. The Cochimí language, which is now extinct, was found to be quite different from the other Yuman languages. Because of this, the whole group was named Yuman–Cochimí. The "Yuman" part refers to all the languages except Cochimí.
Here are some of the languages in this family:
- Cochimí † (This language is no longer spoken.)
- Kiliwa
- Core Yuman languages:
- Delta–California Yuman:
- River Yuman:
- Pai:
- Yavapai
- Havasupai-Hualapai (This includes two main dialects: Hualapai and Havasupai.)
- Paipai (also known as Akwa'ala)
The term "Cucapá" is the Spanish name for the Cocopa people. "Diegueño" is the Spanish name for the Ipai, Kumeyaay, and Tipai languages, which are often called Kumeyaay together. The Upland Yuman languages are spoken by the Yavapai, Hualapai, and Havasupai people. Even though these groups are separate, their languages are very similar and people can usually understand each other.
See also
 In Spanish: Lenguas yumano-cochimíes para niños
In Spanish: Lenguas yumano-cochimíes para niños

