2G facts for kids
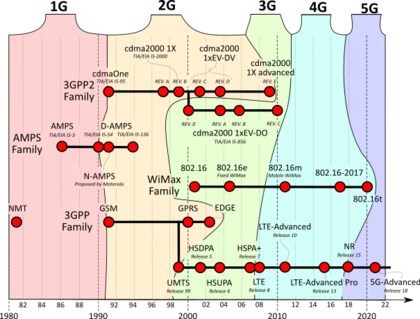
2G stands for "second generation" of mobile phone technology. It started rolling out around the world in the early 1990s. The biggest difference from the first generation (called 1G) was that 2G networks used digital signals instead of analog ones. Think of it like switching from an old radio to a clear digital music player!
This digital change made mobile phones much better. Besides just making voice calls, 2G also allowed for new things like sending text messages and even basic internet on your phone. The most common 2G technology was called GSM, which became popular all over the world. Other 2G technologies included cdmaOne.
Because 2G was digital, it made phone calls and data more secure. It also allowed more people to use the network at the same time. Later versions of 2G, like GPRS, made it possible to have "always-on" internet for things like email. 2G was later replaced by 3G technology, which brought even faster internet speeds.
Contents
How 2G Started
In 1990, engineers at AT&T Bell Labs named Jesse Russell, Farhad Barzegar, and Can A. Eryaman created a patent for a digital mobile phone. Companies like Nokia and Motorola later used their ideas when they were building the first 2G phones.
The very first 2G network was launched in 1991 in Finland by a company called Radiolinja. This network used the GSM standard, which was created in Europe. Another 2G standard, cdmaOne, was first used in 1995.
Later on, 2G networks got upgrades that were sometimes called 2.5G and 2.75G. These upgrades, like GPRS and EDGE, made it possible to send data much faster. GPRS could reach speeds of up to 40 kilobits per second (kbit/s), and EDGE could go up to 384 kbit/s.
Here are the main benefits 2G networks had over the older 1G systems:
- Phone calls were digitally encrypted, making them more private.
- The networks used radio frequencies much more efficiently, meaning more people could use their phones at once.
- New data services became available, starting with SMS text messages and later including MMS (picture messages).
How 2G Got Better
2.5G (GPRS)
2.5G was an improvement to 2G systems that allowed phones to send data in small "packets." This is like sending information in small envelopes instead of one long letter. This technology, mostly known as GPRS, made the network more efficient. It allowed for "always-on" data, meaning your phone could stay connected to the internet without needing to dial up each time. GPRS could reach speeds of up to 40 kbit/s.
2.75G (EDGE)
2.75G was another step up from GPRS, often called EDGE. It made data even faster by using a smarter way to send information. While GPRS was like sending one bit of information at a time, EDGE could send three bits at once! This meant much quicker data speeds. EDGE was first used in 2003 and could reach theoretical speeds of up to 384 kbit/s.
2.875G (EDGE Evolution)
There was an even more advanced version called Evolved EDGE (or 2.875G). This upgrade could reach speeds of up to 1 megabit per second (Mbit/s). It used advanced techniques like using two antennas and special coding to make data transfer faster and more reliable. However, Evolved EDGE wasn't widely used because by the time it was ready, newer technologies like 3G and 4G were already becoming popular.
Why 2G is Being Shut Down
2G has been replaced by newer technologies like 3G, 4G (LTE), and 5G. Even though it's older, 2G networks were still active in many parts of the world as of 2023. However, in places like North America, East Asia, and Australia, many phone companies have already turned off their 2G networks.
Many modern phones that use 4G or 5G can still switch back to 2G for phone calls, especially in countryside areas where newer networks might not be available yet. Interestingly, some companies are turning off their 3G networks before 2G, keeping 2G as a backup for calls. For example, Vodafone turned off 3G in Europe but kept 2G. In the US, T-Mobile also shut down 3G but kept its 2G GSM network.
Many phone companies around the world are planning to shut down their 2G services. This is so they can use the radio frequencies for faster 4G and 5G networks.
One reason 2G is being phased out is that it's considered less secure than newer technologies. Since 2009, people have found ways to exploit weaknesses in GSM networks. Newer phone operating systems like Android 12 and iOS 16 even have settings that let you turn off 2G connectivity on your device for better security.
Why Some People Still Use 2G
Even though 2G is old, it's still used a lot in some places, like the United Kingdom. Many older basic phones still rely on 2G. Also, many "IoT" devices, like smart meters (which send electricity readings automatically) and vehicle trackers, use 2G because it's cheaper and simpler.
If 2G services were completely shut down everywhere, it could cause problems for people who depend on these older phones or devices. They might not be able to make emergency calls or use essential services.
See also
 In Spanish: Telefonía móvil 2G para niños
In Spanish: Telefonía móvil 2G para niños
- Cliff effect
- Dropout
- List of mobile phone generations
- Mobile radio telephone, also known as 0G
- 1G
- 3G
- 4G
- 5G
- 6G
- Wireless device radiation and health
 | Selma Burke |
 | Pauline Powell Burns |
 | Frederick J. Brown |
 | Robert Blackburn |