Aker (deity) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Aker in hieroglyphs |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
3kr He who is beneath |
|||||||||
3kr He who is beneath |
|||||||||
3kr He who is beneath |
|||||||||
| Aker | |||||||||
Aker (also known as Akeru) was an important god in ancient Egyptian beliefs. He was known as the god of the Earth and the horizon. Imagine the horizon as the place where the sky meets the Earth.
Aker had a very special job. He guarded the eastern and western edges of the netherworld, which was the land of the dead.
Contents
Aker's Important Roles
Aker played a key part in the journey of the sun god, Ra.
Protecting the Sun God
Every evening, Ra, the sun god, would travel into the netherworld as the sun set. Aker was there to protect him during this journey. He made sure Ra was safe as he moved through the dark underworld.
Then, in the morning, Aker helped Ra return to the world of the living. He would carry the sun on his back through the underworld, making sure it rose again for a new day. This showed Aker's power over the Earth and the path of the sun.
Guardian of the Deceased
Aker also had a role in helping people who had passed away. He was believed to welcome the spirits of deceased pharaohs. This meant he helped them on their journey in the afterlife.
Power Over Snakes
One of Aker's most interesting powers was his ability to neutralize snake bites. In ancient Egypt, snakes could be very dangerous. People believed Aker could make snake venom harmless. This made him a protector against harmful creatures.
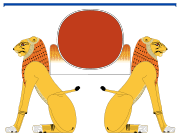
Aker was often shown as a double-headed lion or a sphinx. Sometimes he was shown as two lions sitting back to back. These lions faced opposite directions, representing the eastern and western horizons. This imagery showed his role as a guardian of boundaries.
See also
 In Spanish: Aker para niños
In Spanish: Aker para niños
 | Janet Taylor Pickett |
 | Synthia Saint James |
 | Howardena Pindell |
 | Faith Ringgold |