Alternative splicing facts for kids
Alternative splicing is a clever way our bodies use the same genetic instructions to create many different proteins. Think of it like having a single recipe book, but being able to pick and choose different paragraphs from that recipe to make slightly different dishes.
Our DNA contains genes, which are like instruction manuals for making proteins. When a gene is read, it first creates a temporary copy called messenger RNA (mRNA). This mRNA is made up of important parts called exons and parts that are usually cut out, called introns.
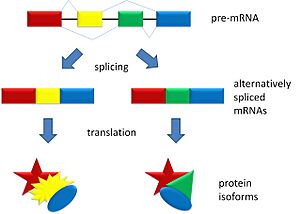
During alternative splicing, these exon parts of the mRNA can be put together in different combinations. This means that from one original gene, you can end up with several unique mRNA molecules. Each of these different mRNA molecules then leads to the creation of a slightly different protein. This process helps our bodies create a huge variety of proteins from a limited number of genes.
Alternative splicing is very common in living things called eukaryotes, which include animals, plants, and fungi. In humans, about 95% of genes that have multiple exons use alternative splicing. This greatly increases the number of different proteins our bodies can make.
How it Works
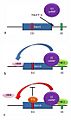
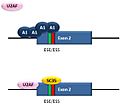
The most common type of alternative splicing is called exon skipping. This is when a specific exon might be included in the final mRNA in some situations or in certain body parts, but completely left out in others.
There are special molecules in our cells that help control this process:
- Splicing activators are like signals that encourage the cell to include a certain exon.
- Splicing repressors are like signals that tell the cell to leave a certain exon out.
Scientists are still discovering new ways that alternative splicing can happen.
Why it Matters
Alternative splicing is a major reason why there is so much variety in the proteins made by eukaryotes. For example, a specific gene in the fruit fly (called DSCAM) can be alternatively spliced into an amazing 38,000 different mRNA versions! This helps the fly's nervous system develop correctly.
Sometimes, mistakes happen during alternative splicing. These abnormal changes can lead to various human genetic disorders. They can also play a role in the development of serious diseases like cancer. When splicing goes wrong and creates non-working proteins, our cells usually have ways to clean them up, often by using special enzymes to break them down.
Images for kids
-
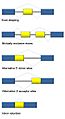
Alternative splicing produces three protein isoforms. Protein A includes all of the exons, whereas Proteins B and C result from exon skipping.
See also
 In Spanish: Empalme alternativo para niños
In Spanish: Empalme alternativo para niños