Aralkum facts for kids

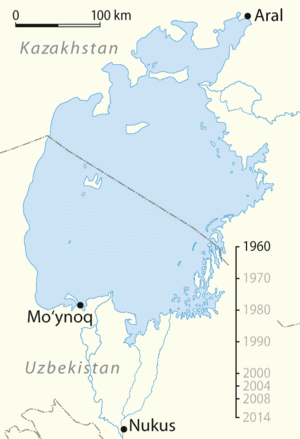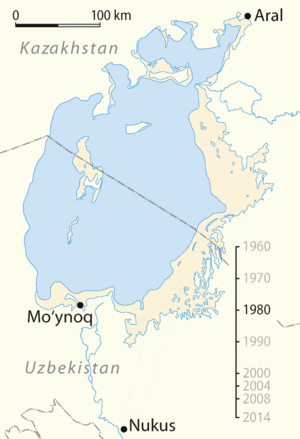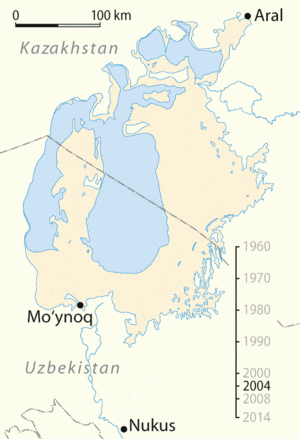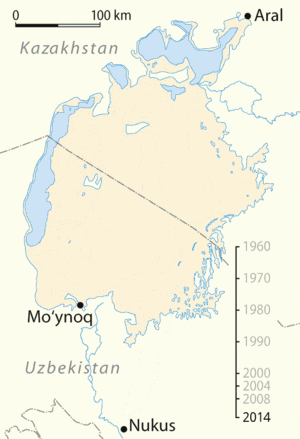
The Aralkum Desert is a new desert that has appeared in Central Asia. It formed in the area where the Aral Sea used to be. This desert lies south and east of what is left of the Aral Sea. It is sometimes called the "Aral Sea Desert" because it grew from the dried-up seabed.
Contents
What is the Aralkum Desert?
The Aralkum Desert is one of the newest deserts in the world. It covers about 60,000 square kilometers (23,000 square miles). This huge area was once covered by the waters of the Aral Sea, which was the fourth-largest inland sea on Earth. As the sea shrank, the exposed seabed turned into a dry, sandy, and salty desert.
How Did the Aral Sea Disappear?
The Aral Sea began to shrink rapidly in the 1960s. This happened because the two main rivers that fed it, the Amu Darya and the Syr Darya, were diverted. These rivers were used to irrigate large farms, mainly for growing cotton, in the dry regions of Central Asia. Less and less water reached the sea, causing it to dry up.
The Cotton Industry's Role
During the Soviet era, there was a big push to grow cotton in the deserts of Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan. Cotton needs a lot of water. To get this water, huge canals were built to take water from the Amu Darya and Syr Darya rivers. While this helped boost cotton production, it had a devastating effect on the Aral Sea. The sea's water level dropped dramatically, and its size became much smaller.
What are the Effects of the Aralkum Desert?
The formation of the Aralkum Desert has caused many serious environmental and health problems for the people living nearby.
Dust Storms and Health
The dry seabed of the Aralkum Desert contains a lot of salt, pesticides, and other chemicals that were used in farming and flowed into the sea. When strong winds blow across the desert, they pick up this salty dust. These dust storms carry harmful particles hundreds of kilometers away. People living in the region suffer from higher rates of respiratory illnesses, cancers, and other health problems because they breathe in this polluted dust.
Climate and Environment
The disappearance of the Aral Sea has also changed the local climate. The sea used to act like a giant air conditioner, making summers cooler and winters milder. Now, without the sea, the region experiences hotter summers and colder winters. This extreme weather makes it harder for plants and animals to survive. Many local species have disappeared, and the unique ecosystem of the Aral Sea region has been severely damaged.
Impact on Local Life
For centuries, fishing was a major industry around the Aral Sea. Thousands of people worked in fishing and related businesses. As the sea dried up, the fishing industry collapsed completely. Many towns that were once busy ports are now far from any water, and their economies have been ruined. This has led to poverty and people moving away from the area to find work.
Can the Aral Sea Be Saved?
While the southern part of the Aral Sea is mostly gone, there have been efforts to save and restore parts of it.
The North Aral Sea Project
Kazakhstan, with help from the World Bank, built a dam called the Kokaral Dam. This dam separates the smaller, northern part of the Aral Sea (often called the Small Aral Sea) from the larger, dried-up southern part. Since the dam was completed in 2005, the water level in the North Aral Sea has risen significantly. Fish populations have returned, and the local fishing industry is slowly recovering. This project shows that with effort, some parts of the environmental damage can be reversed. However, restoring the entire Aral Sea is a much bigger challenge.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Aralkum para niños
In Spanish: Aralkum para niños
 | Emma Amos |
 | Edward Mitchell Bannister |
 | Larry D. Alexander |
 | Ernie Barnes |